If you’ve ever wondered about the difference between electromagnets and permanent magnets, you’re not alone. Choosing the right type of magnet can make all the difference in everything from industrial machinery to everyday gadgets. In this post, you’ll get a clear, straightforward comparison that cuts through the technical jargon to explain how these magnets work, where each shines, and which might be best for your project or application. Whether you’re an engineer, student, or buyer, understanding these magnetic principles is key—and NBAEM is here to guide you with trusted expertise and quality magnetic materials. Let’s dive into the essential distinctions that will help you make smarter, more informed decisions.
What is a Magnet
A magnet is any object that produces a magnetic field, which attracts ferromagnetic materials like iron, nickel, or cobalt. This magnetic field is invisible but powerful enough to influence other magnetic materials and generate force. Magnets are essential components in countless devices and systems we use every day.
What is a Permanent Magnet
A permanent magnet is an object made from material that maintains a constant magnetic field without needing electricity. It works because the magnetic domains inside the material are aligned in one direction, creating a steady magnetic force naturally.
Permanent magnets are often made from materials like neodymium and ferrite, which offer strong magnetic performance. NBAEM specializes in supplying high-quality neodymium magnets known for their powerful and reliable magnetic strength. These materials keep their magnetism over time, making them ideal for long-lasting use.
Some common characteristics of permanent magnets include:
- Strong, consistent magnetic field
- No energy consumption to maintain magnetism
- Durable with good resistance to demagnetization
Typical uses for permanent magnets include motors, sensors, and speakers — devices that require a stable magnetic force without extra power input. NBAEM’s neodymium magnets are especially popular in these areas due to their compact size and high magnetic energy.
What is an Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet where the magnetic field is created by an electric current flowing through a wire coil. When electricity passes through the coil, it generates a magnetic field around it, turning the coil into a magnet. If the current stops, the magnetic field disappears, making electromagnets temporary magnets.
Electromagnets usually have a core made from soft magnetic materials like iron or steel, which helps concentrate and strengthen the magnetic field. The coil windings are tightly wrapped around this core to maximize the effect.
One of the biggest advantages of electromagnets is that you can control their strength by adjusting the electric current. More current means a stronger magnet; less current makes it weaker. This controllability makes electromagnets very useful in many industries.
Common applications include cranes that use electromagnets to lift heavy metal objects, MRI machines where strong magnetic fields are essential for imaging, and electrical relays that rely on controlled magnets to switch circuits on and off. For more on materials used in magnets, check out NBAEM’s detailed insights on soft magnetic materials vs hard magnetic materials.
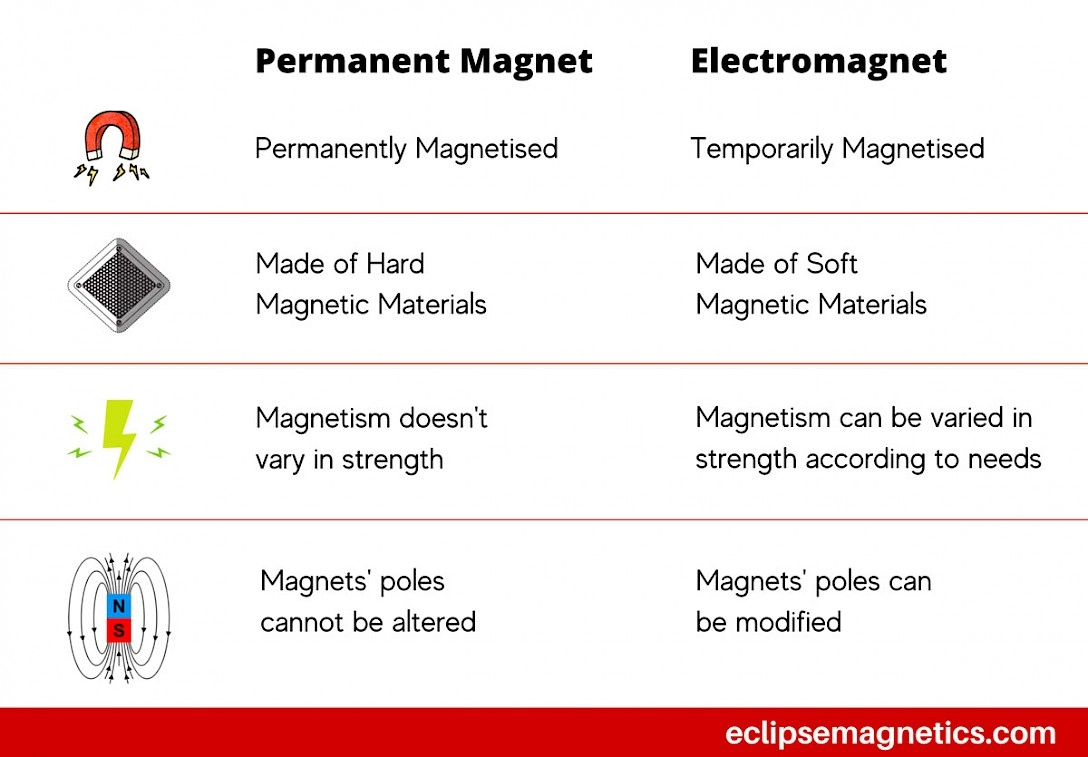
Key Differences Between Electromagnet and Permanent Magnet
Understanding the differences between electromagnets and permanent magnets helps in choosing the right type for your needs. Here’s a breakdown of the main distinctions:
| Feature | Electromagnet | Permanent Magnet |
|---|---|---|
| Source of Magnetism | Electric current flowing through coil | Intrinsic magnetic material |
| Strength | Adjustable by changing current | Fixed strength based on material |
| Control | Can turn magnetism on/off or vary it | Always magnetized |
| Power Consumption | Requires continuous electricity | No power needed |
| Efficiency | Energy used to maintain magnetism | Works without energy input |
| Heat Generation | Can heat up due to current | Minimal heat under normal conditions |
| Operational Limits | Limited by wire heating and power supply | Stable under most conditions |
| Durability and Lifespan | Depends on coil and power source | Long-lasting, little maintenance |
| Cost | Higher initial and operational cost | Usually lower cost over time |
| Size and Weight | Often larger and heavier due to coils | Typically compact and lightweight |
of Differences
- Electromagnets rely on electricity to generate a magnetic field. This allows you to control their magnetic strength and switch them off when needed. However, they consume power, generate heat, and have operational limits based on their design.
- Permanent magnets have magnetism built into their materials like neodymium or ferrite. They don’t need power, are more efficient long-term, and require minimal maintenance but can’t adjust their strength or be turned off.
Choosing between them depends on your application’s need for control, size, energy use, and cost. For example, electromagnets shine in applications requiring on-demand magnetism, while permanent magnets are preferred for steady, maintenance-free magnetic force.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Permanent Magnets
- Maintenance-free: Once installed, permanent magnets don’t need extra power or upkeep.
- No power consumption: They work without electricity, saving energy and reducing costs.
- Compact and lightweight: Great for small devices like sensors, speakers, and motors.
- Reliable magnetic field: Their magnetic strength stays consistent over time without fluctuations.
Advantages of Electromagnets
- Control and flexibility: You can turn them on or off and adjust their strength by changing the electric current.
- High magnetic power: Electromagnets can produce stronger fields than many permanent magnets, which is useful in heavy-duty applications.
- Versatile use: Perfect for applications like cranes, MRI machines, and relays where variable magnetism is needed.
Drawbacks of Permanent Magnets
- Fixed strength: You can’t change the magnetic field once it’s made.
- Limited by materials: Their strength depends on materials like neodymium, which can be expensive or rare.
- Temperature sensitive: Excessive heat can weaken them permanently.
Drawbacks of Electromagnets
- Power consumption: They need constant electricity to work, which can increase operating costs.
- Heat generation: Running current causes heat, requiring cooling systems in some cases.
- Heavier and bulkier: Due to coils and power supplies, they’re usually larger and heavier than permanent magnets.
- Maintenance needs: More components mean more potential points of failure and maintenance requirements.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
When it comes to choosing between electromagnets and permanent magnets, the right pick often depends on the specific application and industry needs.
Where Permanent Magnets Shine
Permanent magnets are preferred in devices that need a constant magnetic field without extra power. They’re common in:
- Motors: Especially in small to medium motors where efficiency and size matter.
- Speakers: To create sound without needing electricity for the magnet itself.
- Sensors: For reliable, low-maintenance magnetic sensing.
NBAEM supplies high-quality permanent magnets like neodymium magnets that are ideal for these applications, offering strong magnetic performance and long-lasting durability.
Where Electromagnets Dominate
Electromagnets are the go-to where magnetism needs to be switched on and off or controlled:
- Industrial cranes: For lifting heavy metal loads, turning magnetism on and off saves energy and adds safety.
- MRI machines: Precise magnetic fields controlled by electricity are crucial here.
- Relays and switches: Electromagnets provide fast, reliable control.
NBAEM’s electromagnets are built with high-grade coil windings and core materials, fitting these demanding industrial uses perfectly.
移除特色图片Choosing Between the Two
- If your application demands constant magnetic strength with low maintenance, permanent magnets from NBAEM are a solid choice.
- If you need adjustable magnetic control or high power on demand, electromagnets from NBAEM provide that flexibility.
Each type plays a vital role across sectors like automotive, electronics, healthcare, and manufacturing, making understanding these differences practical when selecting the right magnet solution.
How to Choose Between Electromagnets and Permanent Magnets
Picking the right magnet depends on a few key factors. Here’s a simple guide based on what you need:
Application Needs
- Permanent Magnets are great when you need a steady, always-on magnetic field without power. Perfect for motors, sensors, or speakers.
- Electromagnets work best when you want control over the magnetic strength or need to turn the magnet on and off. They’re ideal for cranes, relays, or MRI machines.
Budget
| Factor | Permanent Magnets | Electromagnets |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Usually higher upfront due to materials like neodymium | Can be lower but depends on coil and power setup |
| Operational Cost | None – no power needed | Ongoing electricity expenses |
| Maintenance | Minimal | May require more regular checks |
Performance Requirements
- Strength: Electromagnets can achieve high, adjustable magnetic forces. Permanent magnets have fixed strength set by material quality.
- Control: Electromagnets allow you to change or cut off the magnetic field. Permanent magnets don’t.
- Size and Weight: Permanent magnets can be lighter since they don’t need coils or power supplies.
Environmental Considerations
- Heat Sensitivity: Permanent magnets, especially neodymium, lose strength at high temperatures. Electromagnets generate heat but can be designed with cooling solutions.
- Power Supply Access: If electricity is limited or unreliable, permanent magnets are safer.
- Safety: Electromagnets can be switched off to reduce accidents; permanent magnets continuously attract metal nearby.
By matching these points to your project’s needs, you can pick the magnet type that fits best without overspending or compromising on performance.
FAQs Related to Electromagnets and Permanent Magnets
Can electromagnets replace permanent magnets?
Electromagnets can replace permanent magnets in some cases, especially where you need control over the magnetic strength. However, they require power to work, so for simple, always-on uses, permanent magnets are usually better.
Are permanent magnets always stronger?
Not always. Some electromagnets can generate much stronger magnetic fields, especially when powered properly. But permanent magnets like neodymium tend to have strong, consistent magnetic force without electricity.
How does temperature affect both magnets?
High temperatures can weaken permanent magnets and sometimes cause them to lose magnetism permanently. Electromagnets can handle heat better, but overheating the coil can damage the wire insulation or reduce efficiency.
What about lifespan?
Permanent magnets generally last longer since they don’t rely on electricity or moving parts. Electromagnets may wear out faster due to heat buildup or electrical failures but can be repaired or replaced more easily.
Safety tips when handling magnets
- Keep magnets away from sensitive electronics and magnetic storage devices.
- Be careful of pinch hazards, especially with strong magnets.
- Avoid exposure to high heat or impact that can damage the magnet.
- Use insulated gloves if handling large electromagnets connected to power.
These tips keep you and your equipment safe when working with either electromagnets or permanent magnets.



Leave A Comment