Overview for Permanent Magnet Generator: What Makes It Work?
Permanent magnet generators are changing the way we think about energy. Traditional generators are bulky and need constant maintenance. But PMGs offer a simpler and more efficient solution.
A permanent magnet generator uses magnetic fields from permanent magnets to generate electricity, without the need for external excitation or brushes.
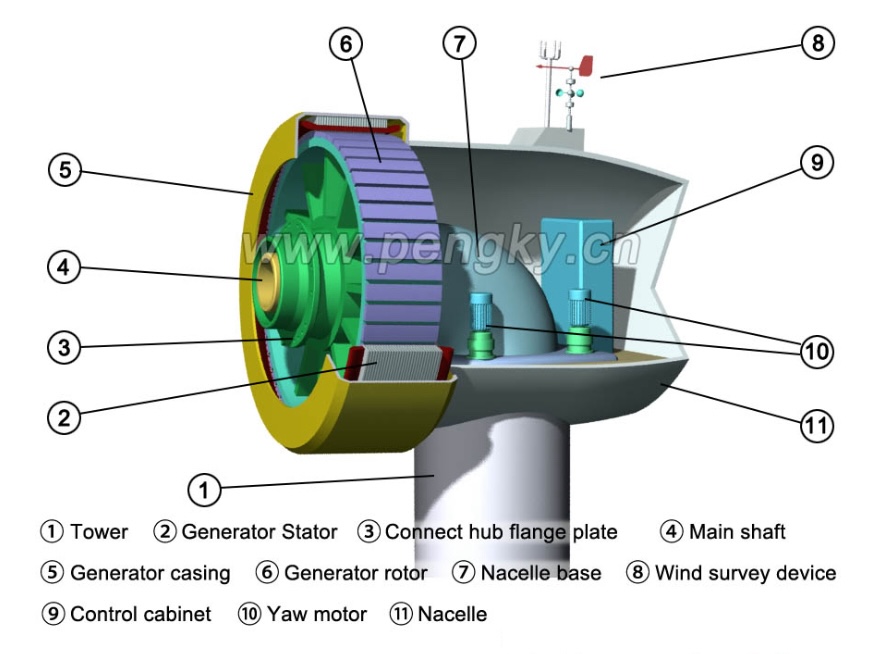
permanent generator(photo from Penky.cn)
If you’re curious about how this type of generator works, or whether you can turn your motor into one, you’re not alone. Let’s break it all down.
How does a permanent magnet generator work?
Most people think generators need complex field coils or external power to work. That’s not always true.
Permanent magnet generators work through electromagnetic induction, using magnets attached to the rotor to induce current in stationary coils.
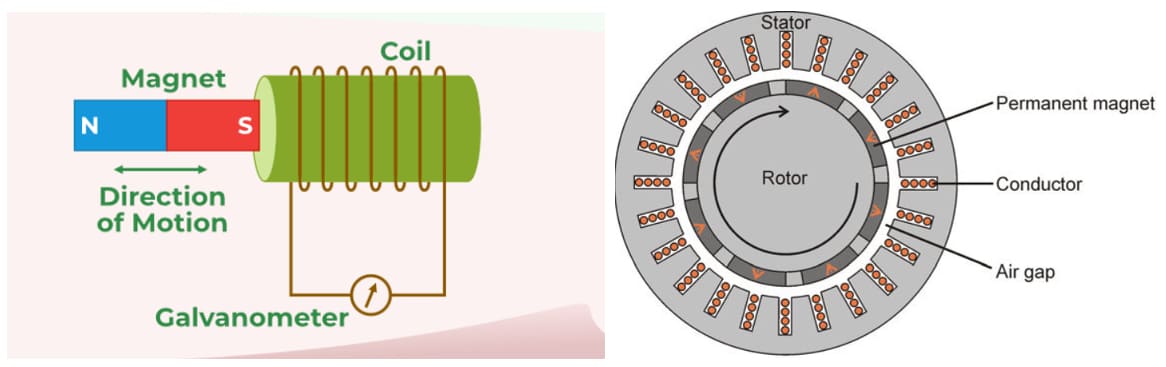
Magnet and Coil Motion & Cross-Section of Rotor and Stator
The Science Behind the Power
Rotor and Stator Setup: In a permanent magnet generator, the rotor contains permanent magnets. These magnets rotate near the stator, which holds copper wire coils. When the rotor spins, it moves the magnetic field around the coils. This movement induces voltage through electromagnetic induction.
Power Output Factors: The strength of the magnetic field, speed of rotation, number of coil windings, and core material all affect how much electricity is generated.
| Factor | Impact on Output |
|---|---|
| Magnet Strength | Stronger magnets = higher voltage |
| Rotor Speed | Faster rotation = more electricity |
| Coil Turns | More turns = higher voltage |
| Core Material | Better permeability = more efficient |
This design eliminates the need for slip rings or brushes. That reduces wear and cuts down on maintenance.
Can a permanent magnet motor be used as a generator?
Many engineers ask this when trying to save time and cost.
Yes, a permanent magnet motor can be used as a generator, but only if designed properly and used in the right setup.
Why It Works and When It Doesn’t
A PM motor and a PM generator share similar components: a rotor with magnets and a stator with coils. When you run electricity through a PM motor, the rotor spins. But if you spin the rotor mechanically, it induces electricity in the stator — just like a generator.
However, there are some differences to consider:
| Feature | PM Motor | PM Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Designed For | Motion output | Electrical output |
| Efficiency Curve | Peak at load RPM | Peak across range |
| Cooling Design | Often for short duty | Often for continuous use |
| Voltage Regulation | External control | Built-in or passive |
In many DIY or small-scale setups, using a motor as a generator works fine. But in critical systems, I recommend using a proper PMG to avoid losses or overheating.
Can a permanent magnet generate electricity?
It sounds like science fiction, but it’s real and already in use everywhere.
Yes, a permanent magnet can generate electricity when it moves relative to a coil, based on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
Not Magic, Just Physics
Magnets don’t generate electricity on their own. They need motion. When a magnet moves near a conductive wire, it causes electrons to move — that’s electric current. This is why PMGs have rotors that spin the magnets past coils.
The electricity generation depends on three key things:
- Magnet strength: Stronger magnets generate more current.
- Speed of movement: Faster motion = higher output.
- Distance from the coil: Closer = stronger induction.
This principle is behind wind turbines, bike dynamos, and even small hand-crank chargers. In each case, the movement of magnets relative to coils creates usable power.
Conclusion
Permanent magnet generators deliver reliable power using simple and efficient principles. They are changing the future of renewable energy, transport, and portable power systems.



Leave A Comment