What Is a Bar Magnet Magnetic Field
Core Definition
A bar magnet is a simple, rectangular piece of magnetic material, usually made from ferromagnetic metals, that produces a magnetic field. It has two distinct ends called poles—north and south—which attract or repel other magnetic materials. The magnetic field is what creates the invisible forces around the magnet that pull on certain metals like iron or steel.
Historical Context
Bar magnets have been used for centuries, dating back to ancient times when people discovered naturally occurring lodestones that could attract iron. Over time, the bar magnet became a fundamental tool for navigation, with sailors using magnetic compasses based on similar principles. The concept helped scientists understand magnetic forces and laid the groundwork for modern magnetic applications.
Key Properties
- Permanent magnet properties: Bar magnets keep their magnetism without needing external power.
- North south poles: Each bar magnet has two poles where magnetic force is strongest.
- Dipole magnetic field: The magnetic field produced is dipolar, with lines flowing from the north pole to the south pole.
- Made of ferromagnetic materials: Common materials include iron, cobalt, nickel, and alloys like NdFeB (neodymium) magnets that offer strong magnetic flux density.
- Attracts and repels: Opposite poles attract; like poles repel.
Understanding the basics of a bar magnet helps us appreciate how magnetic fields work and why these magnets are vital in daily life and industry. If you want to explore further, check out how permanent magnets are used in security systems and energy generation at NBAEM.
The Fundamentals of Magnetic Fields
Definition and Physics Basics
A magnetic field is an invisible force field around a magnet that affects other magnetic materials nearby. For a bar magnet, this field runs from the north pole to the south pole, creating a dipole magnetic field. Think of it as the area where the magnet’s pull or push works. This field is what causes iron filings to line up when sprinkled around a bar magnet, showing the magnetic field lines.
Field Lines Explained
Magnetic field lines are a simple way to visualize the magnetic field around a bar magnet. These lines start at the north pole and curve around to the south pole, never crossing each other. The closer the lines are, the stronger the magnetic field in that area. These lines help us see the direction and shape of the magnetic field, making it easier to understand how magnets interact with other ferromagnetic materials like iron or steel.
Strength Factors
The strength of a bar magnet’s magnetic field depends on several things:
- Material type: Permanent magnets like NdFeB bar magnets are much stronger than regular steel magnets.
- Size and shape: Bigger magnets generally produce a stronger field, but shape also matters.
- Distance: The magnetic field weakens as you move farther from the magnet.
- Temperature: Heat can weaken magnetic properties temporarily.
Comparison Table
| Factor | Effect on Magnetic Field | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Stronger materials produce stronger fields | NdFeB magnets vs regular steel |
| Size | Larger size usually means stronger field | 4-inch vs 2-inch bar magnets |
| Distance from magnet | Field weakens as distance increases | Close to magnet vs several inches away |
| Temperature | High heat weakens magnetic strength | Magnet in a hot environment loses power |
Visualizing the Bar Magnet Magnetic Field
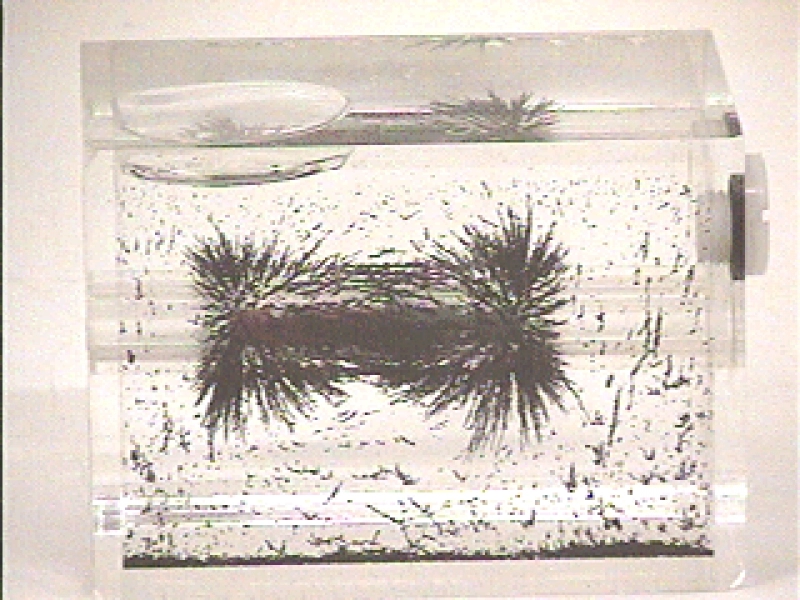

Classic Demonstration
One of the easiest ways to see a bar magnet’s magnetic field is with iron filings. When you sprinkle the filings around the magnet, they line up along the magnetic field lines, showing the dipole magnetic field clearly. This classic demo helps you spot the north south poles and visualize how the field spreads out from the ends of the bar magnet. It’s a simple, hands-on way to grasp permanent magnet properties in action.
Digital Tools
For a clearer and more detailed look, digital tools and apps simulate magnetic fields on your phone or computer. These tools let you adjust the magnet size, type (like NdFeB bar magnets), and see changes in magnetic flux density in real time. They’re great for understanding concepts like the right hand rule magnetism without the mess of iron filings.
Advanced Visualization
In labs or industrial settings, advanced visualization uses sensors and 3D models to map out magnetic fields precisely. This is helpful for engineers working with ferromagnetic materials, checking field strength and direction for bar magnet applications in technology or manufacturing.
Common Misconceptions
- Magnetic fields don’t just start and stop abruptly at the magnet’s poles—they extend around the magnet forming a continuous loop.
- The field lines don’t cross each other.
- Magnetic field strength isn’t uniform; it’s strongest near the poles.
Practical Tip
If you’re experimenting at home or in class, use a flat surface and lightly sprinkle iron filings for the best pattern. Tap the surface gently to help filings align with magnetic field lines. When using digital tools, compare simulations with the classic iron filings demo to deepen your understanding.
Real World Applications and Why It Matters
Everyday Uses
Bar magnets are around us more than you might think. They help keep your fridge magnets stuck and are used in toys, compasses, and small motors. You’ll also find them in household electronics where their magnetic field lines make devices work smoothly. These permanent magnet properties make them reliable for daily use without losing strength.
Industrial Applications
In the industrial world, bar magnets play a big role. They’re used for sorting metals, holding parts in place, and in sensors that detect metal presence. Industries working with ferromagnetic materials depend on strong, durable bar magnets like NdFeB bar magnets for precision tasks. Their dipole magnetic field is powerful yet stable, which is why they’re preferred in manufacturing and recycling processes.
Safety Notes
Handling bar magnets is usually safe, but it’s important to keep them away from sensitive electronics and magnetic storage devices. Their magnetic flux density can disrupt or erase data. Also, strong magnets can snap together quickly, so keep fingers clear to avoid injury.
Innovation Angle
Innovation keeps pushing how bar magnets are used. New materials and designs improve magnetic field strength and durability. For example, advanced magnetic coatings prevent corrosion, extending lifespan. As digital tools help visualize magnetic fields better, designers create more efficient bar magnet applications—supporting clean energy and smarter technology solutions.
Sourcing Quality Bar Magnets Insights from NBAEM
When looking for quality bar magnets, NBAEM stands out as a trusted source. Their selection focuses on premium materials, including NdFeB bar magnets known for strong magnetic flux density and lasting performance. NBAEM ensures each magnet meets strict standards in durability and magnetic strength, ideal for both everyday uses and industrial applications.
Buyer Guide
- Material Type: Choose between neodymium (NdFeB) or ceramic magnets based on your needs. Neodymium offers stronger magnetism but may require protective coatings for durability.
- Size and Shape: Consider the size and dimensions depending on your project; bar magnets come in various lengths and thicknesses.
- Magnetic Strength: Check the product specifications for magnetic field strength and magnetic flux density to ensure it fits your application.
- Coating Options: Look for corrosion-resistant coatings if your application involves moisture or harsh environments.
- Certification: NBAEM provides quality certifications verifying material authenticity and performance.
Why Choose NBAEM
- Wide Range of Magnets: NBAEM offers an extensive variety of permanent magnets suitable for multiple industries and projects.
- Consistent Quality: Rigorous quality control means you get reliable, high-performance magnets every time.
- Competitive Pricing: You get top-grade bar magnets at prices that make sense for both small-scale buyers and large companies.
- Technical Support: NBAEM provides expert guidance to help you select the right magnet for your specific needs.
Call to Action
Ready to find the perfect bar magnet for your project? Explore NBAEM’s selection and experience top-quality permanent magnet properties firsthand. Visit their product pages, like the quality of neodymium magnets, or contact their team today to get started with the best magnets available on the market.



Leave A Comment