The Anatomy of an HDD: Where Magnets Fit In
Ever wondered what makes a hard disk drive (HDD) tick? Inside every HDD, several key components work in harmony to store and read data reliably. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Platos: These spinning discs store your data magnetically.
- Read/Write Heads: Tiny sensors that float just above the platters to read or write data.
- Brazo actuador: Moves the heads across the platters with incredible precision.
- Voice Coil Motor (VCM): The powerhouse that controls the actuator arm’s movement.
Now, where do magnets come into play? The secret lies in the actuator assembly, which uses strong, precise, arc-shaped neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) magnets. These rare earth magnets generate the magnetic field necessary for positioning the read/write heads swiftly and accurately over the spinning platters. Their unique curved shape matches the actuator arm’s arc, optimizing magnetic force while saving space inside the drive.
This magnet placement isn’t just about performance—it’s a reliability cornerstone. In demanding environments like data centers, every millisecond and micrometer counts. The robust magnetic field ensures smooth head movements, helping prevent data errors and mechanical failures. So, those tiny arc-shaped magnets quietly power the heart of your HDD, making sure your data stays safe and accessible day after day.
What Type of Magnets Power Your HDD? A Deep Dive
HDD magnets mainly use neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) rare-earth magnets because they deliver a powerful strength-to-size ratio. This means HDDs get strong magnetic fields in a compact form, essential for precise head positioning and fast data access.
Common NdFeB Grades in HDDs
| Grado | Strength Range | Notas |
|---|---|---|
| N35–N52 | Low to very high | Full NdFeB range |
| N42–N48 | Industry Standard | Most HDDs use these for balance of strength and cost |
| Terbium-doped | Enhanced thermal stability | Better at handling high-temperature environments inside drives |
The terbium doping improves thermal stability, important since HDDs operate from around -40°C to 80°C.
Comparing HDD Magnets Types
| Tipo de imán | Ventajas | Contras |
|---|---|---|
| NdFeB | Strongest, compact, cost-effective | Prone to corrosion (coated) |
| Samario-Cobalto (SmCo) | High temperature resistance, good corrosion resistance | More expensive, weaker than top NdFeB grades |
| Ferrita | Low cost, corrosion-resistant | Much weaker, bulkier |
Even though SmCo magnets handle heat and corrosion well, NdFeB magnets dominate due to their superior power density. Ferrite magnets are mostly outdated for HDD use.
Magnetization Directions and HDD Performance
- Radial magnetization: Magnetized around the arc’s circumference, providing uniform magnetic fields for smooth actuator control.
- Axial magnetization: Magnetized through the thickness of the magnet – used less often but useful in some VCM designs.
The magnetization direction affects how the voice coil motor (VCM) responds, influencing HDD speed and precision. Manufacturers often customize this based on drive design goals.
For more on how magnets operate in precise mechanisms like robotics and actuators, see insights on magnetic actuators for robotic mobility.
This breakdown explains why NdFeB magnets are the go-to choice for HDDs, balancing size, power, and temperature resistance for reliable data storage.
The Evolution of HDD Magnets: From Ferrite to High-Performance Rare Earths
HDD magnets have come a long way since the 1950s. Early HDDs relied on bulky ferrite magnets that were heavy and limited in strength, restricting storage density and precision. By the 1980s, a significant shift occurred with the introduction of neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) magnets. These rare earth magnets offered a much higher strength-to-size ratio, enabling smaller, more powerful actuator arm magnets that improved data accuracy and drive performance.
The rise of technologies like giant magnetoresistance (GMR) and perpendicular magnetic recording (PMR) in the 1990s and 2000s further pushed HDD capacities and speed. These breakthroughs demanded stronger and more stable magnets to precisely position the read/write heads over densely packed data tracks. NdFeB magnets became the industry standard because of their exceptional magnetic strength and reliability under demanding operating conditions.
With solid-state drives (SSDs) gaining popularity, HDD manufacturers adapted NdFeB magnets for roles in hybrid storage systems and high-capacity archival drives. Despite the competitive pressure, HDDs remain crucial in data centers worldwide, relying on high-performance magnets engineered for long life and stability.
Neodymium’s importance in HDDs reflects global rare earth use trends—millions of kilograms of NdFeB have been produced annually to meet the storage industry’s needs. This evolution from ferrite to rare earth magnets marks a key factor in how modern magnetic storage technology has scaled up over decades. For a deeper look at the strength of neodymium magnets used throughout HDDs and other industries, you can explore detailed magnet strength grades at NBAEM’s list of magnets by strength.
Why Neodymium Magnets Excel in HDD Applications: Strength, Precision, and Durability
Neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) magnets are the go-to choice for HDDs thanks to their remarkable power and precision. Here’s why they stand out:
Key Technical Features
- Alta coercitividad: Resists demagnetization even under strong magnetic fields.
- Vibration stability: Keeps magnetic strength stable despite HDD spinning and shocks.
- Wide operating temperature: Performs reliably between -40°C and 80°C, ideal for varying data center conditions.
Aspectos Destacados del Rendimiento
| Característica | Example/Benefit |
|---|---|
| Fuerza de tracción | Strong magnetic force in compact arcs for accurate actuator arm movement |
| Energy efficiency | Enables voice coil motor (VCM) to work precisely with less power |
| Power density | Delivers unmatched magnetic strength for smaller, lighter magnets |
Ventajas y desventajas
| Ventajas | Contras |
|---|---|
| Extremely strong magnets | Susceptible to corrosion (protected by coatings) |
| Precise control of read/write heads | Requires careful manufacturing to maintain quality |
| Durable under constant stress | Costlier than ferrite magnets |
Estudio de Caso NBAEM
NBAEM specializes in custom NdFeB magnet assemblies tailored for HDDs. Their magnets combine high purity and advanced coatings that extend lifespan while preventing rust and performance loss under harsh operating conditions. This ensures HDDs using NBAEM magnets run reliably in critical environments like data centers.
For deeper insight, NBAEM offers resources explaining how neodymium magnets maintain their strength and resist issues common to magnetic materials, such as corrosion (cuánto tiempo duran los imanes de neodimio y magnet rust prevention).
In , NdFeB magnets power HDDs with high strength, precise positioning, and durability in demanding environments, making them irreplaceable for modern magnetic storage technology.
Sourcing and Specifications: Choosing the Right HDD Magnets for Your Needs
When selecting HDD magnets, paying attention to key specs ensures top performance and reliability. Here’s a quick guide:
| Especificación | Rango típico | Por qué es importante |
|---|---|---|
| Tamaño | 20–30 mm arc length | Fits actuator assembly precisely |
| Grado | N42 to N48 NdFeB | Balances strength and thermal stability |
| Revestimiento | Nickel, zinc, epoxy | Protects against corrosion |
| Tolerance | ±0.05 mm | Ensures consistent magnetic force |
High-quality HDD magnets commonly come from reputable Chinese manufacturers like NBAEM, known for supplying high-purity NdFeB magnets with strict certifications. They offer a variety of customization options such as:
- Magnetization patterns: radial or axial to suit different actuator designs
- Hybrid assemblies: combining magnets with soft magnetic materials for enhanced performance
- Volume discounts and pricing: catering to OEMs and bulk buyers
To avoid low-grade imports, look for suppliers with transparent quality control, certification proof, and positive references from the data storage industry. NBAEM’s custom magnet solutions also include advanced coatings and tight manufacturing tolerances to maximize longevity and efficiency in your HDDs.
Beyond Storage: Repurposing and Innovative Uses for HDD Magnets
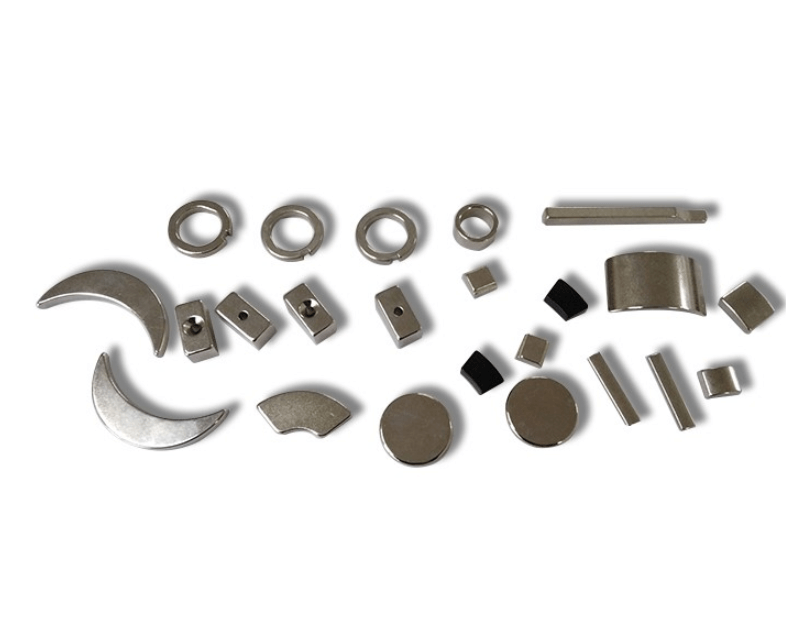
HDD magnets, especially neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) types, are more than just storage components—they have plenty of creative uses once extracted. Safely removing these powerful magnets from old HDDs is simple if you have the right tools. You’ll need a small screwdriver set, pliers, and gloves to protect your fingers from the strong pull.
Once out, these arc-shaped HDD magnets can serve multiple practical purposes:
- Magnetic tool holders for organizing workshop tools
- Robotics sensors where precision magnetic fields are essential
- Microwave oven door latches, using their reliable holding force for safety mechanisms
The versatility of NdFeB magnets extends beyond DIY projects. Their strength and stability make them valuable in electric vehicles (EVs), wind turbines, and various consumer electronics.
From an environmental standpoint, recycling HDD magnets helps reduce e-waste and eases pressure on the rare earth supply chain. Many manufacturers and programs focus on rescuing and reusing these magnets to promote sustainability in tech industries. For those interested in custom magnet shapes and sizes beyond basic HDD uses, NBAEM offers a range of options.
Future-Proofing HDD Technology: Magnets in the Age of SSDs and Beyond
Although SSDs continue to gain ground, HDDs remain vital for large-scale and archival storage, especially in AI data centers. Emerging technologies like heat-assisted magnetic recording (HAMR) rely on magnets that can withstand higher temperatures without losing performance. This demands stronger, more heat-resistant neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) magnets, pushing manufacturers to innovate alloys that last longer under harsh conditions.
The rare earth supply chain poses challenges, but companies like NBAEM are leading with advanced alloy formulations designed to maintain magnet strength and stability over time. Looking ahead, hybrid HDD-SSD systems are likely to become standard, combining fast access with vast storage, all dependent on reliable, high-performance magnets.
For businesses aiming to stay ahead in data storage, working with experts such as NBAEM ensures access to cutting-edge custom neodymium assemblies tailored to future demands. Their expertise helps tackle rare earth constraints while optimizing magnet design for next-gen HDDs and beyond.




Deja un comentario