The Science Behind Magnets A Quick Overview
Magnets may seem simple, but the science behind them powers countless parts of our daily lives. At their core, magnets create an invisible area called a magnetic field, which exerts a force on certain materials like iron, nickel, and cobalt. This magnetic field is what makes magnets attract or repel each other.
There are two main types of magnets you’ll come across:
- Permanent magnets – These keep their magnetic strength over time without needing an external power source. Examples include fridge magnets and magnetic clasps.
- Electromagnets – These generate a magnetic field only when an electric current passes through them. They’re used in powerful machines like MRI scanners, industrial cranes, and electric motors in home appliances.
The principle is simple:
- Opposite poles attract – A north pole connects with a south pole.
- Like poles repel – Two north poles or two south poles push away from each other.
This push-and-pull effect is the secret behind how magnets are applied in everything from keeping your refrigerator door closed to powering speakers and advanced medical devices. The same basic science makes magnets one of the most versatile tools in modern life.
Everyday Household Uses of Magnets

Magnets show up in more places around the house than you might think.
Refrigerator magnets and organization
From holding shopping lists or kids’ artwork on the fridge to keeping reminder notes in sight, refrigerator magnets are a simple but effective way to stay organized. Some even double as small hooks or clips for keys and lightweight items.
Magnetic clasps in jewelry and accessories
Necklaces, bracelets, and some handbags use tiny permanent magnets for easy opening and closing. They’re secure enough to stay fastened but simple to take off without fiddling with small latches.
Magnetic holders for tools and kitchen utensils
A strip of strong magnets in the kitchen keeps knives and metal utensils within reach while saving counter space. In the garage, magnetic tool holders keep wrenches, screwdrivers, and bits organized and easy to find.
Magnetic sensors in doors, windows, and security systems
Many home security and smart home systems rely on magnetic sensors to detect when a door or window is opened. They’re discreet, reliable, and work well for both alarms and automation setups like turning on lights when a door opens.
Magnets in Consumer Electronics and Gadgets
Magnets play a bigger role in our gadgets than most people realize. In speakers and headphones, small but powerful magnets work with coils to move the speaker diaphragm, creating the sound we hear. That same principle is in smartphone speakers, car audio systems, and Bluetooth earbuds.
In everyday appliances like fans, blenders, and washing machines, electric motors rely on magnets to convert electrical energy into motion. Without them, these devices simply wouldn’t run.
Hard drives in older computers use magnets to read and write data, and even modern storage solutions rely on magnetic principles for certain operations. In wireless charging, magnets help align your phone or device with the charging pad so energy transfers efficiently without cords.
From home entertainment to kitchen appliances, magnets quietly keep our tech running smoothly every day.
Medical and Healthcare Applications

Magnets play a big role in modern healthcare. One of the most well-known examples is MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) machines, which use powerful magnets to create detailed images of the inside of the body—helping doctors spot problems without surgery or X-rays.
Some people also turn to magnetic therapy devices, such as magnetic wraps or mattress pads, which are marketed to help with pain relief and circulation. While research on their effectiveness is still ongoing, they remain a popular alternative option.
In advanced medicine, researchers use magnetic nanoparticles to target and deliver drugs directly to problem areas in the body. This approach can make treatments like chemotherapy more precise, reducing side effects and improving results.
Industrial and Commercial Uses Affecting Daily Life
Magnets aren’t just for home gadgets—they play a huge role in industries that impact our everyday lives.
Magnetic separation in recycling and waste management
Recycling facilities use powerful magnets to pull out metals from mixed waste. This makes sorting faster, reduces landfill waste, and keeps valuable materials in use. Without magnetic separation, metal recycling would be far less efficient.
Magnets in electric vehicles and renewable energy
Electric vehicles rely on strong permanent magnets in their motors to deliver smooth and efficient power. Wind turbine generators also use magnets to convert wind energy into electricity. These technologies help lower emissions and support cleaner energy across the U.S.
Magnetic conveyor belts and automated sorting
In warehouses, factories, and shipping centers, magnetic conveyor systems move and organize products more efficiently. They’re also used in food processing to catch stray metal contaminants before products reach consumers.
From recycling plants to green energy projects, magnets quietly keep a lot of modern systems running efficiently.
Emerging and Innovative Uses of Magnets
Magnets aren’t just for fridges and speakers anymore. New tech is pushing their use into areas we wouldn’t have imagined a few years ago.
Smart home devices with magnetic sensors
Many smart locks, security systems, and automated doors use magnetic sensors to detect movement, position, or whether something’s open or closed. They’re quick, reliable, and work without constant maintenance. Even some high-end kitchen appliances use them for safety shutoffs.
Magnetic levitation in transportation
Maglev trains are already in use overseas, and while they’re not common here yet, the idea is gaining attention. These trains use powerful magnets to hover above the tracks, reducing friction for ultra-smooth, super-fast travel. The same concept is being tested in smaller-scale delivery systems.
Robotics and AI applications
In robotics, magnets offer precise movement control and secure holding power without mechanical wear. From factory assembly robots to automated warehouse systems, electromagnets are improving speed and reducing downtime. As AI-driven machines keep evolving, magnets will likely be central to how they move, grip, and interact with their environment.
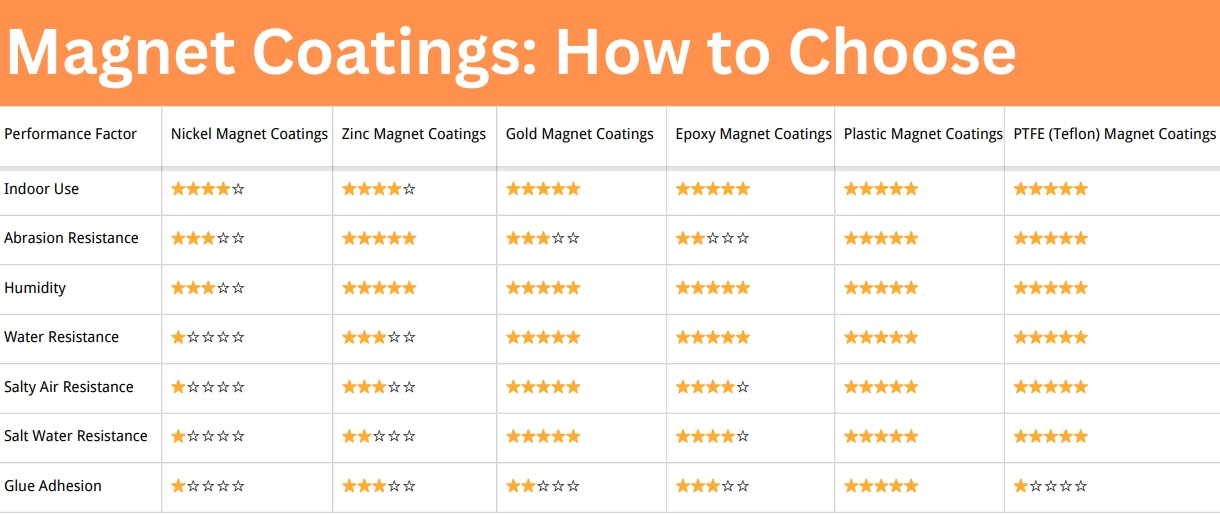
Why Quality Magnetic Materials Matter NBAEM’s Role
When it comes to magnets in everyday products, the quality of the material makes all the difference. Poor-grade magnets lose strength faster, wear out under repeated use, or fail when exposed to heat or stress. That’s why industries from electronics to renewable energy rely on dependable suppliers.
NBAEM has built strong expertise in producing high-quality magnets that meet the durability and performance needs of different applications. From permanent magnets for electric motors to precision magnetic sensors used in consumer electronics, their products are engineered for consistent strength and long-term reliability.
What sets NBAEM apart is its ability to:
- Manufacture magnets to exact performance specs
- Ensure stable magnetic properties under different conditions
- Offer materials suited for both mass production and specialized projects
Their magnets are a key part of supply chains not only in China but also across the U.S., supporting sectors like automotive, medical devices, electronics, and renewable energy. By delivering on both quality and scale, NBAEM helps businesses avoid costly downtime and maintain product performance from the factory floor to the end user.




Leave A Comment