How to create electricity using magnets?
Imagine powering a device without batteries or fuel—just magnets and motion. That idea isn’t science fiction. It’s the basis of electromagnetic induction.
Yes, magnets can generate electricity. When a magnetic field moves past a conductor, it induces a current. This principle powers most generators used today.
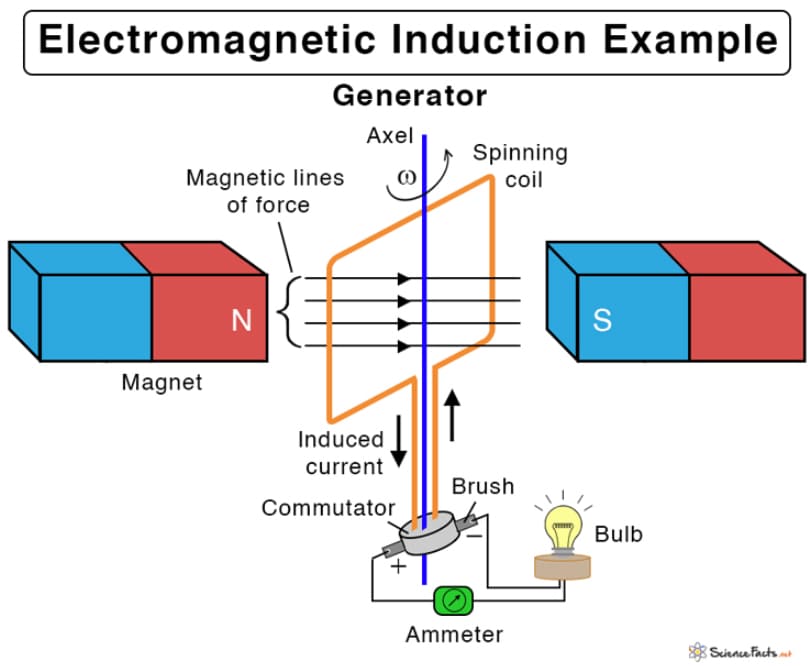
Electromagnetic induction(photo from Sciencefacts.net)
Understanding this can help us unlock how motors, generators, and many electronics actually work.
Is it possible to generate electricity from magnets?
The idea may seem strange at first, but the concept is over 200 years old. When scientists saw electricity and magnetism interact, it changed physics forever.
Yes, it is possible. A changing magnetic field inside a coil of wire produces electricity. This is called electromagnetic induction.
How Does It Work?
1. The Core Concept: Electromagnetic Induction
In 1831, Michael Faraday discovered that a moving magnet near a wire loop induces an electric current. This laid the foundation for electric generators and transformers.
| Element | Role in Induction |
|---|---|
| Magnet | Provides a moving magnetic field |
| Coil (Conductor) | Where voltage is induced |
| Motion | Changes magnetic flux, enabling current flow |
2. Real-World Example: Bicycle Dynamo
When you pedal a bicycle, a small magnet inside the dynamo spins past copper coils. This movement creates voltage, lighting the bike lamp. It doesn’t need batteries—just motion.
3. Faraday’s Law
The strength of the voltage depends on:
- Speed of magnetic field movement
- Number of coil turns
- Strength of the magnet
- Orientation of motion
These factors allow engineers to design different generators for different purposes, from wind turbines to handheld flashlights.
Conclusion
Magnets can create electricity when they move relative to a conductor. This principle is simple but incredibly powerful.




Leave A Comment