The Strongest Permanent Magnet – Neodymium Magnet
Magnets are everywhere, but few people know which one truly leads the pack in strength.
Neodymium magnets are the strongest permanent magnets available today, outperforming all other types in both magnetic strength and energy density.

ring magnet – block magnet – cylinder magnet – magnet with hole
Neodymium magnets changed how we think about magnetic force. Their small size hides incredible power. Let’s explore what makes them so effective—and why they remain unmatched in the market.
What is the highest magnet strength?
Most people think big magnets must be the strongest. That’s not always true.
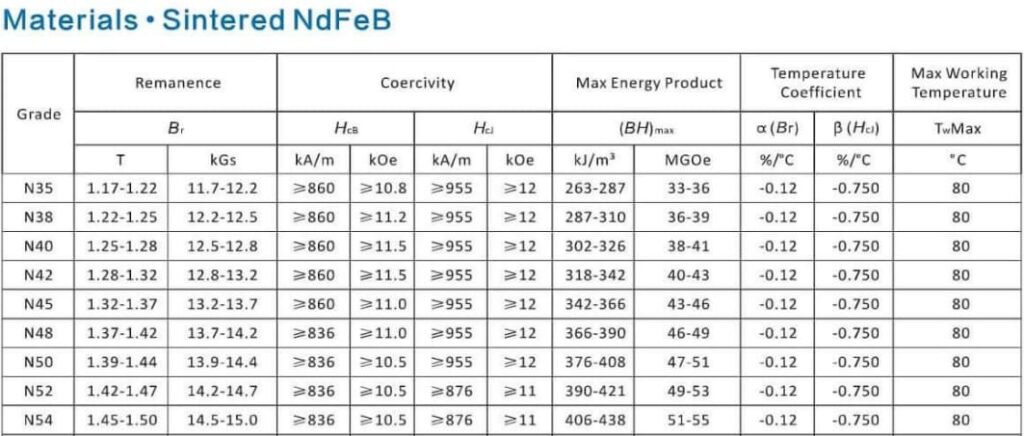
The highest magnet strength comes from neodymium magnets, specifically those with grades like N52, which have energy products over 50 MGOe.We also have N54,N55.
Understanding magnet strength in real terms
To understand magnet strength, I always look at the maximum energy product, or (BH)max. This value tells us how much magnetic energy a material can store. Higher values mean stronger magnets. Neodymium magnets typically range from 30 to 55 MGOe, depending on grade.
Here’s a quick comparison table:
| Magnet Type | (BH)max Range (MGOe) | Relative Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Ferrite (Ceramic) | 3 – 4 | Low |
| Alnico | 5 – 9 | Moderate |
| Samarium Cobalt | 18 – 30 | High |
| Neodymium (NdFeB) | 30 – 55 | Very High |
N55 is the strongest grade commonly used today. Some labs have created higher grades, but they are not widely available due to cost and stability concerns.
What makes a magnet stronger?
Some magnets look alike but perform very differently.
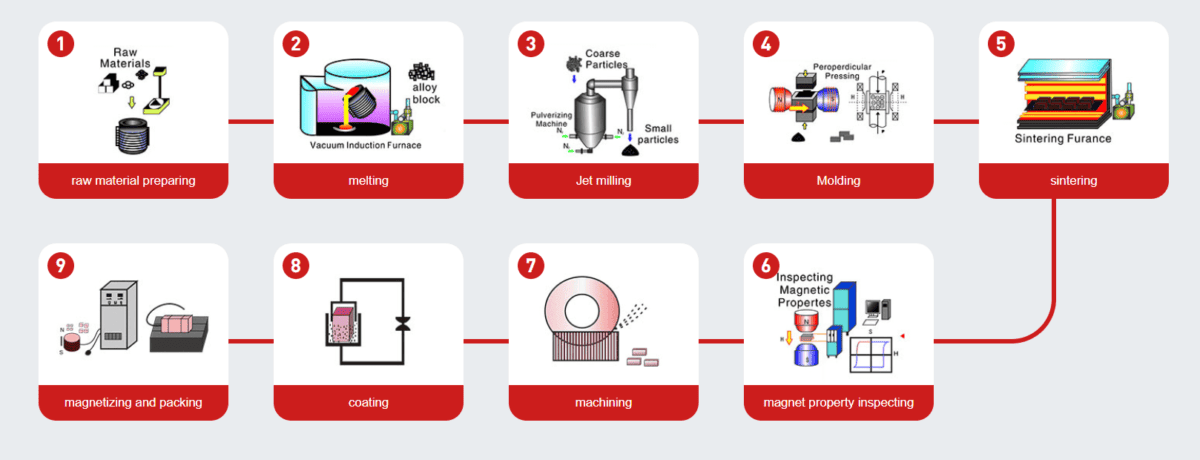
A magnet’s strength depends on its material composition, internal structure, manufacturing process, and grade.
Neodymium magnet production flow
The science behind magnet strength
There are four key factors that influence magnetic strength:
1. Composition
Neodymium magnets are made from a blend of neodymium, iron, and boron (Nd₂Fe₁₄B). This combination creates a very dense magnetic field. Ferrite magnets, by contrast, use strontium or barium and offer far less strength.
2. Crystalline structure
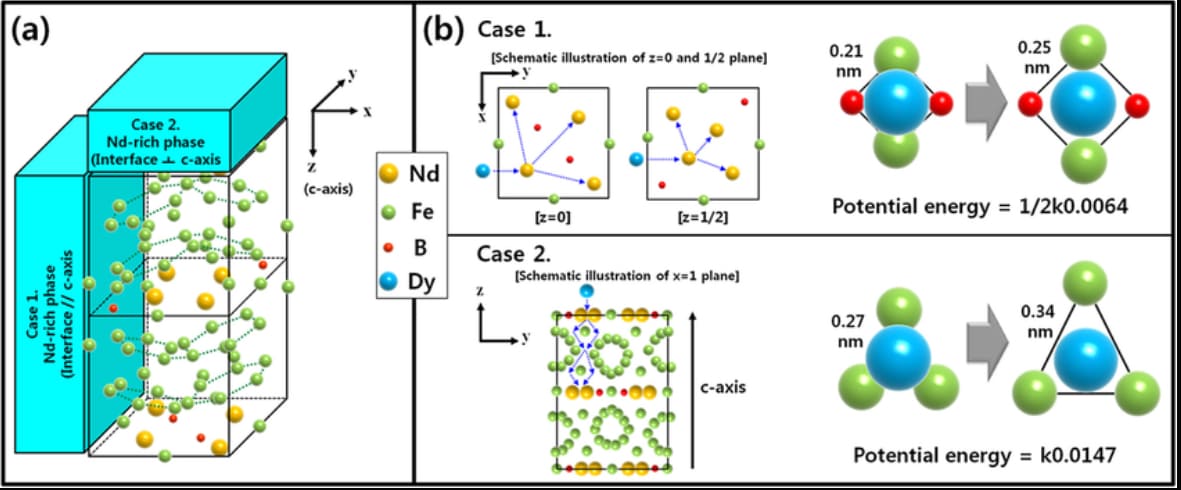
The way atoms align inside the magnet matters. Neodymium magnets have a tetragonal crystal structure that supports high magnetization. This structure helps lock in the magnetic field and resist demagnetization.
Tetragonal crystal structure of Nd₂Fe₁₄B
3. Grade
The grade (like N35, N42, N55) tells us how powerful the magnet is. Higher grades have more magnetic energy per unit volume. But higher-grade magnets are also more brittle and heat-sensitive.
4. Manufacturing quality
Sintering, pressing, and coating methods all impact how the final magnet performs. If the manufacturing process is inconsistent, the magnet may underperform or degrade quickly.
Here’s how these factors compare:
| Factor | Influence on Strength | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Very High | NdFeB is best |
| Crystalline Structure | High | Needs tight control during production |
| Grade | Very High | N55 strongest available widely |
| Process Quality | Moderate to High | Affects stability and durability |
I’ve worked with many suppliers. The best ones always control these four factors with strict QC standards.
Which magnet is most powerful?
Not all magnets are created equal—even within the same type.
Neodymium magnets are the most powerful, and among them, N55 grade offers the highest magnetic performance.
Comparing neodymium grades
Let me share a bit from my daily work. When customers ask for “the strongest magnet,” I usually show them N55 neodymium magnets. These deliver the highest pull force in the smallest size.
But N55 isn’t the best for every use. It can chip easily and loses strength in high temperatures. So I often suggest N42 or N48 for outdoor or motor applications.
| Grade | (BH)max (MGOe) | Strength | Heat Resistance | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N35 | ~35 | Medium | Good | Low |
| N42 | ~42 | High | Better | Medium |
| N55 | ~55 | Highest | Low | High |
If strength is your only goal, go with N55. But if you need balance, N42 is a great choice.
Why are rare earth magnets so powerful?
Most people don’t know why rare earth magnets beat others so easily.
Rare earth magnets use elements like neodymium and samarium, which have unpaired electrons that create strong magnetic fields.
The secret lies in atomic behavior
Rare earth elements, especially neodymium, have unique electron structures. They have many unpaired electrons in their outer shell. This allows for very strong magnetic domains. When aligned, these domains generate high magnetic flux.
There are two main types of rare earth magnets:
- Neodymium magnets (NdFeB): Strongest, but sensitive to heat and corrosion.
- Samarium cobalt magnets (SmCo): Strong and stable at high temperatures, but more expensive.
| Rare Earth Magnet | Max Energy (MGOe) | Temp Resistance | Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| NdFeB | Up to 52 | Low | Low |
| SmCo | Up to 32 | High | High |
I’ve seen many industries switch to rare earth magnets to reduce size and increase efficiency, from motors to medical tools.
Conclusion
Neodymium magnets remain unmatched in strength, making them the top choice for high-performance magnetic applications.




Buon giorno, come posso fare per calcolare la forza di repulsione fra due magneti cilindrici al neodimio N55 in dipendenza della distanza dei magneti stessi?. se avete qualche tabella con queste misure ve ne sarei grato.