Project Description
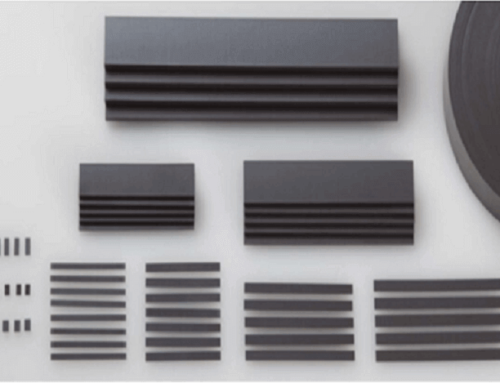
Laminated magnet

Laminated magnets are also known as segmented magnets. They are made of two or more individual magnets bonded yet insulated to each other. Laminated NdFeB magnet were developed for the purpose of enhancing the performance of electric machines. This is achieved by preventing the magnets from overheating. In addition to NdFeB, SmCo magnet is also commonly applied in the magnet segmentation technology.
Technical background of laminated magnets
With the development of electric motors for vehicles and generators for wind power constructions, the demand for sintered NdFeB magnets is growing fast. Being the main components of these devices, NdFeB magnets enable them to work at high speed. However, eddy current will be produced during the high-speed operation in the magnets and consequently cause NdFeB magnets to heat up. As a result, demagnetization takes place when the temperature in the magnets reaches a certain point. By segmenting complete NdFeB blanks and then laminating them together with adhesive, each magnet becomes an independent part and insulates each other. This will effectively reduce eddy current loss and keep down the temperature of NdFeB magnets during the operation
How magnet segmentation fights against demagnetization
One drawback of NdFeB magnet is its poor resistance to high temperature. The magnets demagnetize at high temperature. By laminating and insulating NdFeB blank, the eddy current path is broken into several paths. Thus, it reduces the eddy current density and eddy current loss decreases as well.
Two types of laminated magnets
Depending on the technical requirement in the application, individual NdFeB magnets are glued together to form complete laminated NdFeB magnets either before or after coating.
The Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) shown above belongs to “after-coating type”, where individual magnets are coated and then glued in a certain way to form a larger unit. So-called “before-coating type” is shown on the right. This type typically requires a much complicated technique and is more expensive to make.
Key processing technique of laminated magnets
To start with, a NdFeB blank is sliced (segmented) into several single pieces of the same thickness and laminated with glue for the purpose of insulation. Then the whole laminated NdFeB blank is treated as a normal blank, which is to be cut, sliced and ground into the desired geometry and dimension. It has to be noted that the bonding adhesive typically achieves maximal 95% insulation. Also, the final product – a complete laminated NdFeB magnet can’t be electroplated because the magnet, after placing adhesive inside the magnet body, is no longer as conductive as to be properly electro-coated. Instead, epoxy-painting (usually black) is often used as an alternative coating solution.
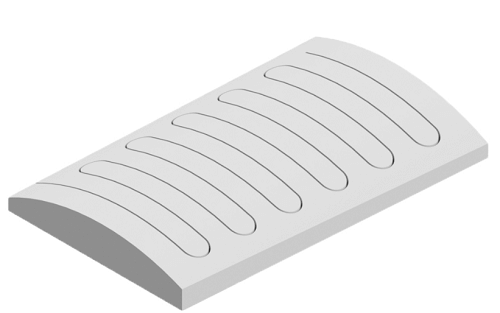
Another technology-Snakeline Magnets
This design is from Bomatec.
Laminated magnets require hours of manual labor and produce a significant amount of waste. Snakeline magnets simplify this process. Industrial-precision wire EDM machines create cuts in the finished magnet, eliminating the traditional methods of slicing, stacking, and re-gluing magnets together. This efficient process results in time saved and less material waste, especially required with expensive samarium cobalt magnetic material. With our proprietary epoxy filling technique already mature and deployed with our manufacturing partners, Bomatec has the capacity to quickly and efficiently deploy a Snakeline process across your design.
REQUEST A QUOTE
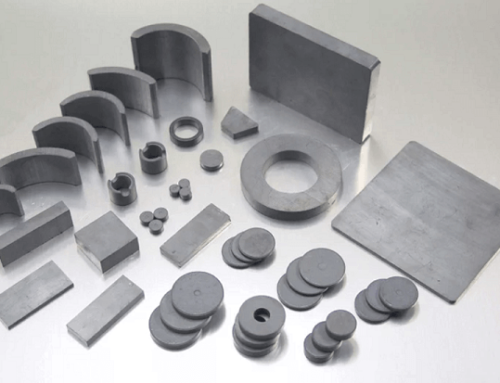
Looking for a certain size? Please see the different sizes of magnets as follows. If you require a specific size that is not available on our website, please contact us for a custom neodymium magnet quote.