What Are Round Magnets
Round magnets are circular magnetic discs commonly used in a wide range of consumer, industrial, and technical applications. They are one of the most popular magnet shapes because they provide a uniform magnetic field across their flat surfaces, making them reliable for both holding and sensing tasks.
These magnets can be solid discs (without a hole) or holed discs (with a bore or countersunk opening for mounting). They vary in size, strength, and material to meet different needs.
Understanding Dimensions and Terminology
When choosing round magnets, a few size measurements are essential to know:
- Diameter – The distance across the circular face of the magnet.
- Thickness – How tall the magnet measures from one flat side to the other.
- Bore size – The diameter of any central hole, if present.
Precise dimension details are crucial since magnet strength and application compatibility depend heavily on size.
Common Materials Used
Round magnets are manufactured from different magnetic materials, each with its own properties:
- Neodymium (NdFeB) – The strongest type, ideal for maximum holding power in small sizes.
- Ceramic (Ferrite) – Cost-effective, corrosion resistant, and suitable for general use.
- Alnico – Resistant to high temperatures, often used in sensors and instruments.
Material choice directly impacts magnetic strength, durability, and cost.
Round Magnets Without Hole Features and Applications
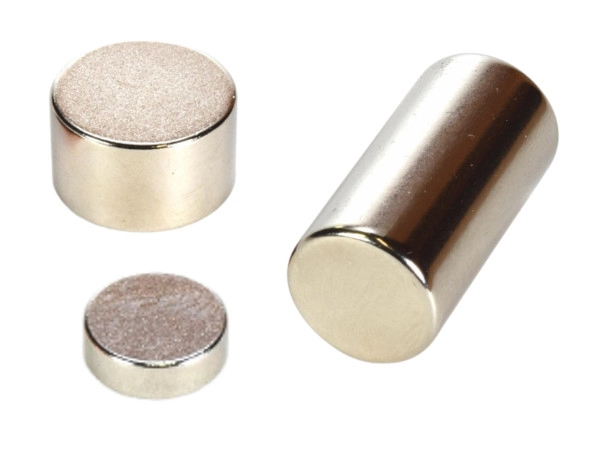

Round magnets without a hole are solid magnetic discs made entirely of magnetic material. Since there’s no drilled center, they keep maximum surface area and magnetic mass intact, giving them stronger pull strength compared to magnets with holes of the same size.
Benefits of solid round magnets:
- Stronger magnetic force – all material contributes to the magnetic field.
- Simpler design – no extra machining, making them reliable for direct use.
- Lower cost – less manufacturing work compared to magnets with drilled or countersunk holes.
Common uses in the U.S. market:
- Holding and fastening – securing metal tools, displays, or equipment.
- Motors and generators – used where high magnetic strength is needed.
- Sensors and electronics – for position sensing and control systems.
- Craft projects and home repairs – easy to handle and affordable.
Limitations to consider:
- No built-in mounting point – needs adhesive, brackets, or custom holders.
- Can be harder to align mechanically in some assemblies.
- May require coating (like nickel or epoxy) for corrosion resistance in humid environments.
Quick reference for common materials:
| Material | Strength | Cost | Rust Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neodymium | Very high | Higher | Low (needs coating) |
| Ceramic/Ferrite | Medium | Low | Good |
| Alnico | Medium-High | Higher | Excellent |
These solid round disc magnets without hole are the right fit when you need maximum magnetic strength and a clean, simple form—especially for applications where mechanical fastening isn’t required.
Round Magnets With Hole Features and Applications
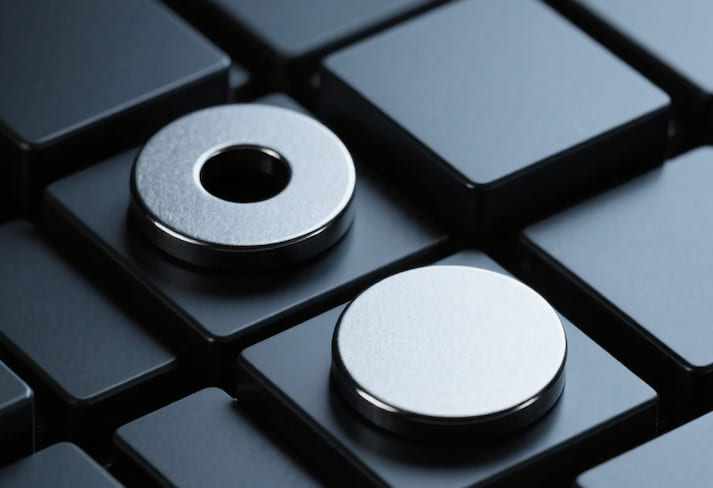

round magnets with hole and without hole
Round magnets with a hole in the center—whether it’s a straight through hole or a countersunk hole—are designed for easy mounting. The hole lets you attach them with screws, bolts, or rivets directly to a surface. This makes them a favorite in setups where you need a magnet to stay firmly in place without shifting.
Benefits
- Easy installation – Secure with simple hardware like screws or bolts.
- Versatile mounting – Works on wood, metal, or plastic surfaces.
- Better mechanical stability – Holds position even under vibration.
- Neat integration – Countersunk holes allow flush screw heads for a cleaner finish.
Common Uses
- Motors – For fixed placement of magnetic parts.
- Door latches and catches – Keeps panels or doors closed securely.
- Electronic devices – For sensors or mounted components.
- DIY projects – Perfect for work that needs reliable mounting without glue.
Types of Holes and Their Impact
| Hole Type | Description | Magnetic Strength Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Through hole | Simple round hole; fits standard screws or bolts | Slight reduction |
| Countersunk | Angled hole so screw heads sit flush with surface | Slightly more reduction due to larger cutout |
Because part of the magnetic material is removed to make the hole, strength is typically a bit lower than a solid disc magnet. Still, for many applications, the trade-off is worth the secure and permanent mounting option.
Key Differences Between Round Magnets With Hole and Without Hole
When choosing between round magnets with a hole and without a hole, a few core differences stand out. These can affect how strong the magnet is, how you install it, and even the cost. Here’s a quick breakdown.
Magnetic Strength and Field Impact
- Without Hole: Solid round magnets keep their full surface area, so they usually deliver stronger pull force.
- With Hole: The hole removes some magnetic material, so pull force is slightly reduced. How much depends on hole size and magnet material.
| Type | Magnetic Strength | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Without Hole | Stronger | Full contact area, no material removed |
| With Hole | Slightly less | Material removed for mounting hole changes flux path |
Installation and Mounting
- Without Hole: Requires glue, metal brackets, or magnetic holders to mount.
- With Hole: Designed for quick mounting with screws, bolts, or rivets. Countersunk holes sit flush for a clean finish.
Weight and Cost
- Without Hole: More material means slightly heavier. Often cheaper to produce since no extra machining is needed.
- With Hole: Lighter due to less material. Can cost more because of the drilling or countersinking process.
Best Fit by Industry or Environment
- Without Hole:
- Strong holding applications (industrial lifting, magnetic clamping)
- Consumer products that don’t need mechanical fasteners
- Motor and sensor setups where strength is key
- With Hole:
- Installations needing secure, mechanical fastening (door latches, mounting plates)
- Electronics enclosures or motor mounts
- Outdoor uses where screws prevent magnet slipping
How to Choose the Right Round Magnet for Your Project
When picking between round magnets with hole or round magnets without hole, you’ll want to zero in on a few practical factors. Getting it right the first time saves time, cost, and hassle.
Key Factors to Consider
- Magnetic Strength – Neodymium offers the strongest pull; ceramic is more affordable but weaker.
- Mounting Needs – Choose holed magnets if you need to screw or bolt into place; solid discs work best for free-hanging or magnetic contact applications.
- Environment – For outdoor or humid areas, go with materials like coated neodymium or stainless-backed assemblies to prevent rust.
- Corrosion Resistance – Nickel, epoxy, or rubber coatings extend life in tough conditions.
- Size and Fit – Match diameter, thickness, and hole size (if applicable) to your space and required holding power.
- Budget – Solid magnets generally cost less; magnets with holes can be slightly higher due to added machining.
Application Recommendations
| Use Case | Magnet Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Education | Ceramic or small neodymium without hole | Safe and cost-effective for classroom demos |
| Industrial | Large neodymium with hole or countersunk | Easy mounting to metal or machinery |
| Home Use | Mix of both types | Solid for fridge/boards, holed for DIY fixtures and mounts |
Why Supplier Reliability Matters
Magnets may look similar, but quality varies a lot between suppliers. Watch for:
- Consistent grades that match advertised strength
- Accurate dimensions for proper fit
- Coatings that last under real-world conditions
- Quality certifications (ISO, RoHS) for safe and compliant use
For long-term projects, sourcing from a trusted magnetic materials supplier ensures you’re getting the right pull force, durability, and fit every time.
Why Choose NBAEM for Your Magnetic Material Needs
NBAEM has years of experience supplying high‑quality magnets to industries, makers, and small businesses across the U.S. We understand the difference the right magnet makes, whether you’re building equipment, designing products, or working on a DIY project.
Wide Product Range
We offer round magnets with hole and round magnets without hole in a variety of sizes, grades, and materials, including Neodymium, Ceramic, and Alnico. You can find both standard stock items and custom‑made options to match your exact specifications.
| Product Type | Available Sizes | Material Options | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Round Magnets Without Hole | 5mm to 100mm diameter | Neodymium, Ceramic, Alnico | Holding, fastening, motors, crafts |
| Round Magnets With Hole | 5mm to 80mm diameter | Neodymium, Ceramic | Mounting with screws, sensors, door catches |
Quality and Customization
- Tight tolerance manufacturing for consistent performance
- Custom hole sizes, shapes, and coatings available
- Strong magnetic grades for demanding applications
Competitive Pricing
As a direct China supplier, NBAEM offers cost‑effective pricing without cutting corners on quality, making it easier for U.S. buyers to get premium magnets at a fair cost.
Customer Service and Support
- Quick response to inquiries
- Technical guidance on choosing and installing magnets
- Reliable after‑sales service for repeat orders and replacements
With NBAEM, you get the magnetic materials you need, in the right size and strength, backed by a supplier that understands both industrial and individual project needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can the hole size be customized
Yes. Manufacturers, including us, can produce round magnets with custom hole sizes and shapes—whether it’s a simple through hole or a countersunk style for flat-head screws. Just keep in mind that changing the hole size can affect both strength and cost.
How much does the hole reduce magnetic strength
A hole removes material, which does slightly reduce the pull force compared to a solid magnet of the same size. The effect depends on the hole’s diameter—small holes have less impact, while larger holes can noticeably lower strength.
Are magnets with holes more expensive
In most cases, yes. The extra machining or molding to add a hole increases production costs. The price difference is usually small for standard sizes but higher for custom designs or strong rare-earth types like neodymium.
What mounting hardware is recommended
For through holes, use standard bolts, screws, or threaded rods that fit the inner diameter. For countersunk holes, flat-head screws provide a flush mount. Stainless steel hardware is best if you need corrosion resistance.
How to install round magnets securely
- Clean both the magnet and the mounting surface.
- Use non-magnetic bolts to avoid interference.
- For high-vibration areas, add a washer or locking nut.
- Apply epoxy or thread-locking adhesive for extra hold.
- Make sure the magnet is not over-tightened to prevent cracking, especially with brittle neodymium magnets.




Leave A Comment