Understanding the Role of Speaker Magnets
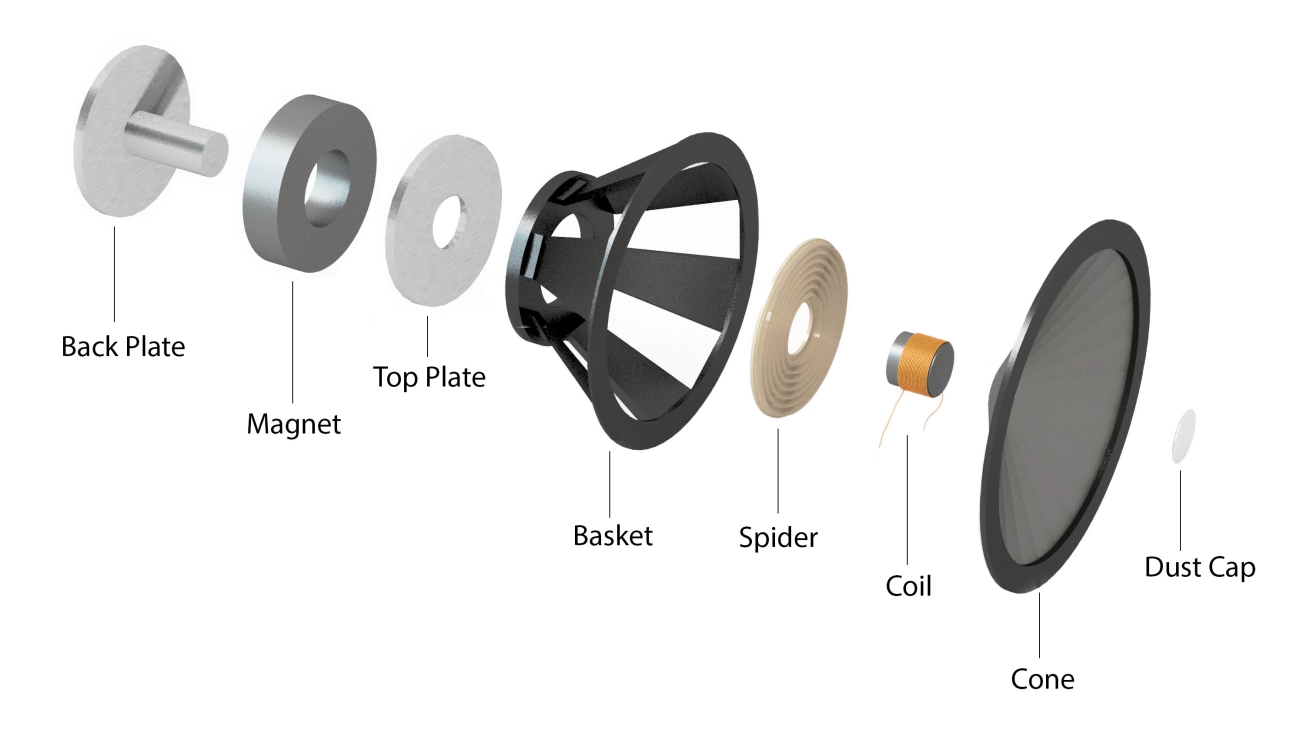
If you have ever wondered what actually drives the sound in your speakers, the answer starts with the speaker magnet. Every dynamic speaker relies on a magnet to convert electrical energy into the movement that creates sound. The magnet works hand in hand with the voice coil and cone to produce clear, accurate audio.
speaker magnet
What is a speaker magnet
A speaker magnet is the static magnetic field source inside a loudspeaker. It creates the magnetic gap in which the voice coil moves. When an audio signal (electrical current) passes through the voice coil, it interacts with the magnet’s field, causing the cone to move back and forth, generating sound waves.
How magnets influence speaker sound quality and efficiency
The strength, size, and material of the magnet can dramatically affect performance:
- Magnetic strength impacts sensitivity and efficiency, meaning stronger magnets can produce louder sound with less power.
- Material type influences tone characteristics. For example, neodymium magnets tend to deliver tight, detailed sound, while ferrite can provide a warmer tone in some designs.
- Weight and size play a role in portability and design flexibility, especially important for compact or high-powered speakers.
Basic physics behind speaker magnets and voice coil interaction
The process is rooted in electromagnetism:
- An electrical signal flows through the voice coil.
- This creates an alternating magnetic field around the coil.
- The coil’s field interacts with the static field from the speaker magnet.
- Attraction and repulsion between these fields move the coil forward and backward.
- The attached cone pushes and pulls air, creating the sound waves you hear.
A well-matched magnet and voice coil system means better sound accuracy, efficiency, and reliability, whether it’s in a small portable speaker or a high-performance subwoofer.
Key Types of Speaker Magnets
Ferrite magnets
Ferrite magnets are made from iron oxide mixed with ceramic compounds. They’re produced through a sintering process, which makes them durable and cost‑effective. Ferrite is heavier than other magnet types, but it’s stable even under high temperatures.
Pros:
- Affordable and widely available
- Good resistance to demagnetization
- Performs well in larger speaker designs like subwoofers
Cons:
- Heavier than neodymium
- Lower magnetic strength for the same size
Common uses: Budget-friendly home audio systems, car speakers, PA systems, and subwoofer speakers where weight isn’t a main concern.
Neodymium magnets
Neodymium magnets are made from an alloy of neodymium, iron, and boron. They deliver a much stronger magnetic field than ferrite, even in a smaller size. This lets manufacturers design lightweight, compact speakers without losing power.
Pros:
- High magnetic strength in a small size
- Lighter weight for portable or compact designs
- Ideal for high-performance audio and tight spaces
Cons:
- More expensive than ferrite
- Can lose strength at very high temperatures if not coated or shielded
- Vulnerable to corrosion without protective plating
Common uses: Premium headphones, stage monitors, high‑end home audio, and lightweight portable speakers where space and performance matter.
Alnico magnets
Alnico magnets are made from aluminum, nickel, and cobalt. They were popular in vintage speakers before ferrite and neodymium became common. Alnico produces a smooth, warm tonal character some musicians and audiophiles prefer.
Pros:
- Excellent tonal quality with a natural sound
- Strong magnetic stability over time
- Performs consistently across a wide temperature range
Cons:
- More expensive and heavier than ferrite
- Lower magnetic strength compared to neodymium for the same size
Common uses: Guitar amp speakers, specialty studio monitors, and vintage‑style audio gear where tone is more important than size or weight.
Other Emerging and Specialty Speaker Magnet Materials
When it comes to speaker magnetic materials, most people think of ferrite, neodymium, or alnico. But there are also newer and specialty magnet options being explored for specific performance needs.
Samarium Cobalt Magnets
Samarium Cobalt (SmCo) magnets have a high magnetic strength similar to neodymium but with much better temperature resistance and excellent corrosion protection. This makes them reliable in environments with extreme heat or humidity where ferrite and neodymium might lose magnetism over time. They’re more expensive, so they’re often used in high-end, professional-grade audio equipment where long-term stability matters more than cost.
Composite Magnets
Composite magnets are blends of magnetic materials with resins or polymers. They’re not as powerful as metal-based magnets, but they provide lighter weight and design flexibility for portable speakers, Bluetooth devices, and custom shapes that are hard to produce with traditional magnets. They also resist chipping and cracking, making them more durable for consumer electronics.
New Magnetic Materials in Research
Researchers are looking into rare-earth alternatives due to rising costs and supply concerns. Some areas of interest include:
- Ceramic-rare earth hybrids for mid-range performance at lower cost
- Recyclable magnetic materials to reduce electronic waste
- High-temperature alloys that maintain performance in demanding conditions
These developments aim to create durable magnet types for audio equipment without sacrificing sound quality or efficiency.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Speaker Magnet
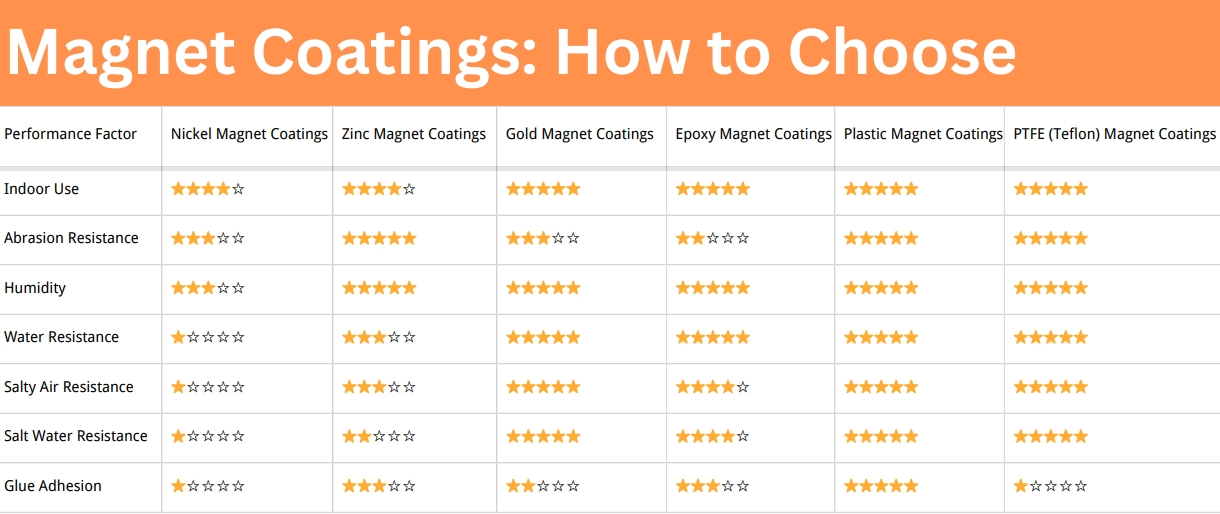
When picking the right magnet for a speaker, a few key things can make or break the design. The type of magnet you choose directly affects sound, size, durability, and cost. Here’s what to keep in mind:
Magnetic Strength and Sound Quality
- Stronger magnets provide better control over the voice coil, which can improve clarity, volume, and bass response.
- High-performance speaker magnets like neodymium offer strong magnetic fields even in small sizes, while ferrite provides solid performance at a lower cost.
Size and Weight in Speaker Design
- Lightweight speaker magnets are key for portable audio gear, car speakers, and touring equipment.
- Larger, heavier magnets can improve sound in stationary setups but may not be ideal for compact designs.
Environmental Durability
- Consider temperature resistance for speakers used outdoors or in hot environments.
- Corrosion resistance matters for marine audio or humid conditions — some magnets like ferrite handle moisture better than others.
Cost and Availability
- Ferrite magnets are widely available and affordable, making them popular for mass production.
- Neodymium offers top performance but at a higher price and with more market fluctuations.
Compatibility with Manufacturing
- The chosen magnet must fit your production process, whether you’re working with a simple speaker magnet manufacturing process or need custom shapes and coatings.
- Some magnets require more specialized handling or assembly steps, which can affect lead times and cost.
How NBAEM Supports Speaker Manufacturers with Magnetic Materials
NBAEM has built a solid reputation as a trusted magnetic materials supplier in China, providing speaker manufacturers in the U.S. and worldwide with reliable, high-performance solutions. We specialize in speaker magnetic materials for different applications – from compact consumer audio devices to large subwoofers. Our product portfolio covers ferrite, neodymium, alnico, and specialty magnets designed to meet specific sound quality, weight, and durability needs.
We work closely with OEMs and audio brands to deliver customizable magnet solutions. This includes tailoring magnetic strength, size, coating, and thermal resistance so the final speaker design hits exact performance targets. Whether you need lightweight speaker magnets for portable gear or high-performance magnets for professional audio setups, we adjust manufacturing specs to match your product goals and production workflow.
Over the years, we’ve partnered with several U.S. and global audio brands to optimize speaker magnet manufacturing processes. In one case, we helped a professional studio monitor manufacturer switch from ferrite to neodymium for improved clarity and reduced cabinet weight. In another, we supplied corrosion-resistant ferrite magnets for outdoor PA systems, boosting durability without increasing costs. These real-world results show how our materials directly improve performance, efficiency, and product lifespan for speaker makers.
Frequently Asked Questions About Speaker Magnets
Which magnet type is best for high-end audio speakers?
Most premium speaker brands lean toward neodymium magnets for high-end systems. They’re smaller, lighter, but have a much stronger magnetic field, which translates into better control over the speaker cone and improved clarity. Some audiophiles still like Alnico for its warm, vintage sound, especially in guitar amps and retro-style speakers.
Can magnets affect speaker longevity?
The magnet itself usually lasts decades without losing noticeable strength, unless it’s exposed to extreme heat, strong opposing magnetic fields, or physical damage. What affects speaker life more are the other components (like the cone and suspension), but poor magnet design or material quality can impact performance stability over time.
How does magnet size impact sound?
Generally, a larger magnet means more magnetic force, which can help with higher efficiency and deeper bass—especially for subwoofers. But it’s not just about size; the magnet’s material, field strength, and overall speaker design matter just as much. A strong neodymium magnet, for example, can outperform a much bigger ferrite magnet in certain setups.
Are there eco-friendly or recyclable magnet options?
Ferrite magnets are easier to recycle and don’t rely on rare earth materials, making them a greener choice. Some companies are also developing alternative magnetic materials that reduce rare-earth use while keeping performance high. If sustainability matters, ask your magnetic materials supplier about recycling programs or reclaimed material options.
You can also read more about different magnet types and properties here: Overview for types of magnets.




vorrei mettermi in contatto con voi , a me serve l’intelaiatura più il magnete del diffusore . la mia e mail : fotienrico09@gmail.com.