What Exactly Are Magnetic Tools?
Magnetic tools use magnets to attract, hold, lift, or organize metal objects—usually ferrous metals like iron or steel. At their core, these tools harness magnetic fields, created by aligned magnetic domains inside magnet materials, to generate a pulling force. This magnetic force picks up screws, holds parts steady, or lifts heavy metal sheets, making many tasks faster and safer.
Core Mechanics of Magnetic Tools
- Magnetic domains: Tiny regions inside a magnet where atoms align to produce a magnetic field.
- Magnetic field: The invisible force that pulls ferrous metals toward the tool.
- Polarity: Dictates how magnets attract or repel (critical when holding or releasing objects).
This simple magnetic principle revolutionizes tools by adding magnetic power to traditional designs.
Magnetic Tools vs Traditional Tools
| Feature | Magnetic Tools | Traditional Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Quickly pick up/find small parts | Manual searching or handling |
| Safety | Holds metal parts securely | Risk of dropping or losing parts |
| Versatility | Multi-use: pickup, holding, lifting | Designed for single tasks |
| Maintenance | Low—no moving parts needing repair | May require lubrication or parts replacement |
| Eco-friendliness | Reusable with no batteries or fuel | Some require batteries or power |
Evolution of Magnetic Tools & NBAEM’s Role
Magnetic tool technology has come a long way—from simple fridge magnets to powerful neodymium magnets engineered for heavy-duty use. NBAEM has been a game-changer in this evolution, developing high-performance magnetic grades that boost pull strength while keeping tools lightweight and durable.
Core Types of Magnetic Tools
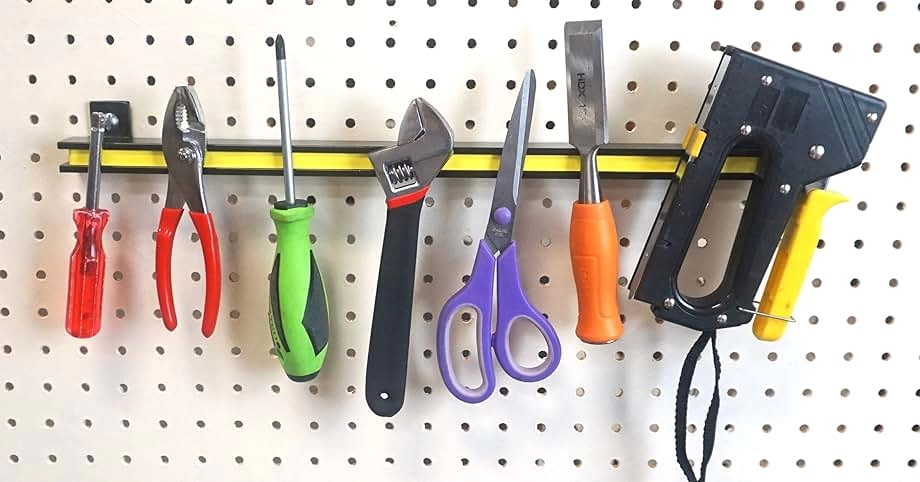

Magnetic tools come in a few main types, each designed for specific jobs around the garage, workshop, or factory.
Pickup and Retrieval Tools
These are your go-to magnetic pickup tools like telescopic wands and flexible probes. Some come with LED lights, making it easier to grab small metal parts from tight or dark spots.
Magnetizers and Demagnetizers
These handy devices let you magnetize screwdriver tips or demagnetize them when needed. Perfect for keeping screws in place or preventing unwanted metal shavings from sticking.
Lifting and Holding Devices
Heavy-duty magnetic lifters are built for handling sheet metal and other ferrous parts safely and efficiently. Magnetic weld clamps and industrial chucks also hold materials steady during fabrication or assembly.
Workshop Organizers and Sweepers
Magnetic trays, racks, and wheeled sweepers keep your workspace clean by organizing tools and picking up metal debris fast. Great for any busy shop or home garage.
Specialized Fixtures
These include specialized magnetic clamps, holders, and chucks designed for welding or machining tasks, providing reliable grip and precision.
Selection Guide for Different Users
| Use Case | Tools Recommended | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Home DIY | Telescopic pickup wands, magnetic trays | Lightweight, easy to use |
| Pro Mechanic | Magnetizers, LED retrieval tools, lifters | Durable, ergonomic |
| Industrial Use | Heavy-duty lifters, chucks, weld clamps | High pull force, heavy-duty |
This breakdown helps pick the right magnetic tools whether you’re fixing a bike in Dallas or running a busy shop in Detroit.
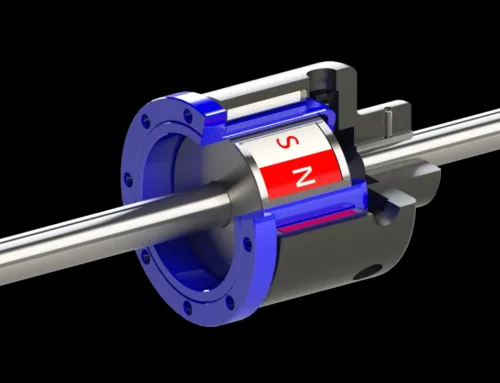
How Magnetic Tools Work
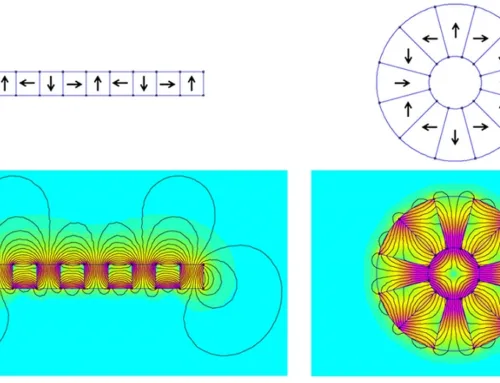
Magnetic tools work by using magnets to attract and hold onto metal objects, mainly those made of iron, steel, and other ferrous metals. At the core, magnets have tiny regions called magnetic domains. When these domains line up in the same direction, the magnet creates a magnetic field with a specific polarity—north and south poles—which gives the tool its pulling power.
Magnetic Domains, Polarity, and Field Strength Explained Simply
- Magnetic domains: Small areas inside a magnet where atoms’ magnetic moments align.
- Polarity: Every magnet has a north and a south pole; opposite poles attract ferrous metals.
- Field strength: The stronger the alignment of domains, the more powerful the magnet’s grip.
Step-by-Step Usage Guide for Magnetic Tools
- Identify the metal item you need to pick up or hold—remember, magnetic tools only work on ferrous metals.
- Place the magnetic tool near or against the metal part.
- Magnet activates automatically by attracting the item.
- Secure the object: For lifting or holding devices, ensure a firm grip before moving.
- Release by removing the tool or using a demagnetizer if included.
Neodymium vs Ceramic Magnets
Neodymium magnets are the powerhouse of magnetic tools—small but mighty. They deliver stronger magnetic pull compared to ceramic magnets, which are bulkier and less powerful but still budget-friendly for basic uses.
- Neodymium magnets: High strength, perfect for professional mechanics and industrial use.
- Ceramic magnets: Good for light-duty tasks like home DIY and simple garage needs.
Common Myths About Magnetic Tools Addressed
- Myth: Magnetic tools damage electronics.
Fact: Properly used, magnetic pickup tools have minimal risk around electronics. - Myth: Magnets lose strength quickly.
Fact: High-quality magnets like those from NBAEM maintain strength for years if cared for. - Myth: Magnetic tools attract all metals.
Fact: Only ferrous metals respond; aluminum or plastic won’t stick.
NBAEM’s Magnetic Grades for Performance
NBAEM supplies magnets classified by their strength and quality. Their advanced neodymium grades deliver reliable, long-lasting pull power, favored in US workshops and industrial settings. Choosing NBAEM’s magnetized tools means consistent performance tailored to your specific needs, from light pickup wands to heavy-duty ferrous part lifters.
Real-World Applications of Magnetic Tools
Magnetic tools have become a go-to in garages, factories, and homes across the U.S. Whether you’re a mechanic, a DIYer, or working in industrial settings, these tools save time and reduce hassle. Take the example of a welder in Texas who switched to magnetic weld clamps and magnetized tool tips from NBAEM. His workflow sped up significantly because he didn’t have to constantly reposition heavy parts or hunt for dropped screws.
Here’s why magnetic tools are popular:
- Efficiency: Quickly pick up nuts, bolts, and metal scraps with magnetic pickup tools or telescopic retrievers.
- Safety: Heavy-duty ferrous part lifters and weld holding clamps hold parts steady, cutting down on accidents.
- Versatility: From mini screwdriver magnetizers to industrial magnetic chucks, there’s a tool for almost every metalworking or organizing job.
Users often praise NBAEM’s precision inserts and magnets for keeping their tools strong and reliable, even after heavy daily use. In workshops, magnetic trays and sweepers make clean-ups faster and more thorough, improving overall productivity.
If you work with metal parts regularly, magnetic tools are more than a convenience—they’re a smart investment.
Pros, Cons, and Smart Buying Tips for Magnetic Tools
Magnetic tools offer several clear advantages that make them popular in US garages, workshops, and industrial settings. Here’s what you should know before buying:
Pros
- Durability: Magnetic tools, especially those with Neodymium magnets, last long and resist wear.
- Low Maintenance: No need for batteries or power, and magnets don’t usually wear out quickly.
- Eco-Friendly: Reusable and don’t require chemicals or disposable parts.
- Safety: Helps keep metal parts in place or off floors, reducing injury risks and improving workspace organization.
Cons
- Ferrous-only: Magnetic tools only work with ferrous metals (iron, steel). They’re useless on aluminum, copper, or plastic parts.
- Demagnetization: Strong heat or shocks can weaken magnet strength over time, especially with Neodymium tools.
- Magnet Interference: Can affect electronics or credit cards if not handled carefully.
Smart Buying Tips
- Pull Rating: Check the magnet’s pull force to ensure it matches your lifting or holding needs. A higher pull rating means stronger grip.
- Ergonomics: Choose tools with comfortable grips and easy handling, especially for extended use.
- Warranty: Opt for brands that offer warranties, which is a mark of quality and durability.
- Budget Tiers:
- Entry Level: Affordable for occasional home use, usually ceramic magnets.
- Mid-Range: Balances cost with power, often with better magnet grades and features.
- Premium: Uses high-performance Neodymium magnets, ideal for pros and industrial use. NBAEM’s premium sourcing ensures top magnet quality and consistency.
Beware of Fakes
Magnetic tools are popular, so counterfeits exist. Stick to certified suppliers and trusted brands like NBAEM to avoid low-quality magnets that lose power fast or break easily.
For more on magnetic materials and how to pick the right magnet strength, check out NBAEM’s guide on magnetic technologies.
Maintenance and Best Practices for Magnetic Tools
Keeping your magnetic tools in top shape is simple if you follow a few easy steps:
Cleaning and Storage Tips
- Wipe your magnetic pickup tools, telescopic retrievers, and workshop debris sweepers regularly with a dry cloth to remove dust and metal shavings.
- Avoid using water or harsh chemicals, as moisture can weaken magnets or cause rust on metal parts.
- Store magnetic tools separately in a dry, cool spot away from electronics or credit cards to prevent damage.
- Use protective cases or trays, especially for neodymium magnet tools, to avoid knocks that reduce magnet strength.
Troubleshooting Weak Magnetism
- If your tool loses pull power, check for metal debris stuck to the magnet and clean it off.
- Strong impacts, extreme heat, or improper storage near other magnets can cause demagnetization.
- For screwdriver magnetizers or demagnetizers, re-magnetize the tool tip as needed following the product instructions.
- If problems persist, consider testing with NBAEM’s magnetic grades replacement inserts for restored performance.
Safety Precautions
- Handle heavy-duty ferrous part lifters and magnetic chucks carefully—strong magnets can pinch skin or attract tools quickly.
- Keep magnets away from pacemakers, sensitive electronics, and credit cards.
- Use gloves when dealing with larger weld holding clamps or magnetized work surfaces to avoid injury.
- Always follow manufacturer guidelines for maximum pull force and tool use.
By sticking to these maintenance and safety tips, your magnetic tools will work reliably across US garages, workshops, and industrial settings for years to come.



Leave A Comment