Are you concerned about what are the negative effects of magnets on the human body? You’re not alone. With magnets found everywhere—from household gadgets to medical devices—understanding their impact on our health is more important than ever. While magnets have many beneficial uses, questions about their safety and potential risks keep popping up.
In this guide, you’ll get clear, evidence-based insights into how magnets actually interact with the human body, what science says about potential side effects of magnetic exposure, and practical steps to stay safe. Whether you’re curious about magnetic field health effects, worried about magnets and pacemaker safety, or just want the facts behind the myths, we’ve got you covered.
Let’s break down the facts from fiction and explore what you really need to know about magnets and your health.
Scientific Background of Magnets and the Human Body
Magnets create magnetic fields, invisible forces that affect certain materials and living tissues. Magnetic fields have two main characteristics: strength (measured in teslas or gauss) and type. There are static magnetic fields, generated by permanent magnets that stay constant, and electromagnetic fields, which vary with electrical currents.
Human tissues contain ions and charged particles, making them responsive—albeit minimally—to magnetic fields. The biological interaction depends largely on the field’s strength and duration of exposure. For example, weak magnetic fields from household magnets cause negligible effects, while strong fields, such as those in MRI machines, can influence ion movement and nerve cell activity.
Static magnets produce constant fields, whereas electromagnetic fields change over time and can induce electrical currents in the body. Understanding these differences is key to assessing any potential health risks associated with magnetic field exposure.
Potential Negative Effects of Magnets on Human Health
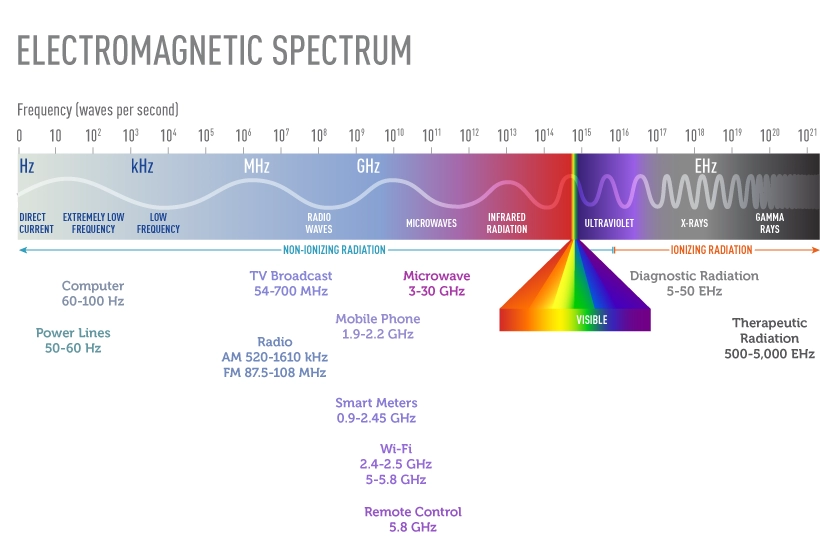
Some people worry about the side effects of magnetic exposure, especially when it comes to strong magnets or electromagnetic fields. Commonly reported symptoms include headaches, dizziness, and a general feeling of discomfort after being near powerful magnets. While these symptoms are often mild and temporary, they shouldn’t be ignored if they persist.
One of the biggest concerns is how strong magnetic fields can interfere with medical devices like pacemakers and implantable defibrillators. These devices rely on precise electrical signals, and strong magnets can disrupt their function, posing serious health risks. That’s why people with these implants are advised to keep a safe distance from magnets and magnetic machinery.
At a cellular level, very intense magnetic fields may affect biological tissues, potentially altering cellular processes or blood flow. However, these effects mostly occur under high exposure conditions that aren’t common in everyday life or typical household magnets.
There are also claims about magnets impacting the nervous system, sometimes suggesting they cause neurological symptoms. Most of these claims are exaggerated or not backed by solid evidence. In fact, mild symptoms some people report can often be explained by psychological or placebo effects rather than any real magnetic influence.
Overall, while strong magnets deserve respect and caution—especially around medical devices—everyday exposure from household magnets or low-level fields generally doesn’t cause harmful health effects if used properly.
Scientific Evidence and Research Findings
When it comes to magnets and the human body risks, science helps clear up a lot of confusion. Numerous studies and meta-analyses have looked into the safety of magnetic exposure, especially focusing on how magnetic fields affect health. The good news is that low-strength household magnets—those you find in things like fridge magnets or small gadgets—pose little to no risk to most people. These everyday magnets create weak magnetic fields that our bodies handle without trouble.
On the other hand, high-strength magnets, which are used in medical machines like MRI scanners or industrial equipment, can have stronger effects. Research shows that strong magnetic fields may influence biological tissues and interfere with devices like pacemakers. That’s why there are safety rules around exposure. But for healthy individuals, the risk from these high-strength magnets is still low if proper precautions are followed.
It’s important to note though that some gaps and controversies remain. For example, scientists are still studying whether long-term exposure to moderate magnetic fields could have subtle effects on the nervous system or cellular processes. Some findings are mixed, and more research is needed to fully understand these risks.
In , current scientific evidence suggests that everyday magnet exposure is mostly safe, but caution is key when dealing with powerful magnets or people with medical devices.
Misconceptions and Myths about Magnets and Health
There are plenty of myths floating around about magnets causing serious health problems like cancer, infertility, or permanent damage. But the truth is, these claims don’t have solid scientific backing. Many of these stories come from misunderstanding how magnetic fields work or from marketing magnetic therapy products without real evidence.
Some common myths include:
-
Magnets cause cancer or tumors
No credible research supports magnets triggering cancer or tumor growth.
-
Magnets lead to infertility
There’s no proven link between everyday magnetic exposure and reproductive health issues.
-
Magnets can permanently harm your organs
Except for some medical device interference, magnets do not cause lasting organ damage.
Distinguishing pseudoscience from facts means looking for studies and trusted sources, not just anecdotal claims or unverified online info. If you’re curious about how magnets truly affect health, it’s best to check out reputable scientific reviews rather than social media or marketing hype.
For reliable info on magnet properties and safety, consider resources like the detailed overview of types of magnets which highlight real scientific facts instead of myths. This helps you make smarter choices and avoid unnecessary fears about magnetic exposure.
Safety Guidelines for Using Magnets
When it comes to magnets and health, safety is key. Here are some straightforward tips to keep in mind when handling magnets, whether at home or work.
Safe Handling and Exposure Limits
- Avoid prolonged close contact with strong magnets—while household magnets are generally safe, high-strength magnets can cause physical injuries like pinching or affect sensitive equipment.
- Keep magnets away from electronic devices that might be damaged by magnetic fields.
- Use magnets in well-ventilated areas and avoid stacking strong magnets, which can cause sudden snapping that might lead to injuries.
Precautions for Vulnerable Groups
- Children should never play unsupervised with strong magnets, as swallowing magnets can be extremely dangerous.
- Pregnant women should avoid unnecessary exposure to strong magnetic fields, especially from industrial sources.
- People with pacemakers or implantable medical devices must be extra careful. Strong magnets and electromagnetic fields can interfere with these devices, risking serious health problems. Always follow medical advice and device manufacturer guidelines.
Best Practices for Industrial and Consumer Use
- Use magnets that meet established safety standards. If you’re buying from suppliers like NBAEM (a well-known Chinese magnetic material supplier), confirm that their products comply with relevant safety regulations.
- Properly label magnetic materials and provide clear warnings especially in industrial settings.
- Train employees and consumers on safe magnet handling to prevent accidents.
Following these safety guidelines will help reduce the risks associated with magnetic field exposure while still allowing you to benefit from the many useful aspects of magnets in daily life.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While most everyday exposure to magnets, like those in household items, is generally safe, there are times when you should be alert for warning signs related to magnet exposure. If you notice symptoms such as persistent headaches, dizziness, nausea, or any unusual sensations after handling strong magnets or being near medical magnetic devices, it’s a good idea to take these seriously.
Here’s when you should consider seeing a doctor:
- If you have a pacemaker or implantable medical device and experience interference symptoms like irregular heartbeat, dizziness, or shortness of breath after magnet exposure
- If you develop unexplained neurological symptoms, such as numbness or weakness after being around strong magnets
- If symptoms like headaches or dizziness persist beyond a short period after magnet contact
- If you suspect a magnet has disrupted a medical device or procedure
Healthcare professionals play a key role in diagnosing and managing any magnet-related health concerns. They can review your symptoms, evaluate your exposure level, and run necessary tests to rule out other causes. If you have implanted medical devices, always inform your doctor about your magnet exposure history. Prompt medical advice helps prevent complications linked to magnetic interference or other risks.
Remember, don’t hesitate to seek medical help if magnet exposure causes uncomfortable symptoms or affects your medical devices. Your safety is the top priority.




cuántos gaus puede soportar el cuerpo